
ECSS system
Glossary of terms
Foreword
The ECSS Glossary is part of the series of ECSS Standards intended to be applied together for the management, engineering and product assurance in space projects and applications. ECSS is a cooperative effort of the European Space Agency, national space agencies and European industry associations for the purpose of developing and maintaining common standards.
Requirements in ECSS Standards are defined in terms of what shall be accomplished, rather than in terms of how to organize and perform the necessary work. This allows existing organizational structures and methods to be applied where they are effective, and for the structures and methods to evolve as necessary without rewriting the standards.
This document has been prepared by the ECSS Glossary Task Force, reviewed and approved by the ECSS Technical Authority.
Traceability to the previous ECSS Glossary “ECSS-P-001B” is ensured through the matrix given in Annex A.
Disclaimer
ECSS does not provide any warranty whatsoever, whether expressed, implied, or statutory, including, but not limited to, any warranty of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose or any warranty that the contents of the item are error-free. In no respect shall ECSS incur any liability for any damages, including, but not limited to, direct, indirect, special, or consequential damages arising out of, resulting from, or in any way connected to the use of this Standard, whether or not based upon warranty, business agreement, tort, or otherwise; whether or not injury was sustained by persons or property or otherwise; and whether or not loss was sustained from, or arose out of, the results of, the item, or any services that may be provided by ECSS.
Published by: ESA Requirements and Standards Division
ESTEC, P.O. Box 299,
2200 AG Noordwijk
The Netherlands
Copyright: 2012© by the European Space Agency for the members of ECSS
Change log
|
ECSS-P-001A
|
First issue
|
|
ECSS-P-001A Rev.1
|
First issue, Revision 1
|
|
ECSS-P-001B
|
Second issue
|
|
ECSS-S-ST-00-01C
|
Third issue
|
Scope
This document controls the definition of all common terms used in the European Cooperation for Space Standardization (ECSS) Standards System. Terms specific to a particular ECSS Standard are defined in that standard.
This document does not include the definition of terms used with their common meaning. In this case, the definition from the Oxford English Dictionary applies.
Terms, definitions and abbreviated terms
Terms and definitions
When using the ECSS standards, the following is the order of precedence of documents as the source of definition of terms:
-
the standard in question
-
the present Glossary of terms
-
the Oxford English dictionary.
A term used within a definition, which is defined elsewhere in this document is shown in boldface. A boldface term may be replaced within the definition by its own definition.
A concept that has a special meaning in a particular context is indicated by designating the context in angle brackets, < >, before the definition.
A document reference shown after a definition in square brackets, [ ], indicates that this definition is reproduced from the referenced document.
For example:
All terms and their definitions appear in alphabetic order in clause 2.3 of this Glossary. However, wherever it is considered important to present together a set of terms that are interrelated (i.e. constitute a particular “view”), these terms and their definitions are repeated in standalone sections of this Glossary or in Annexes. For example, clause 2.2 collects together all terms that relate to the breakdown of the overall Space System.
Space system breakdown
Introduction
ECSS-S-ST-00C defines the highest-level system within a space project – i.e. the one at the mission-level - as the “Space System”. The purpose of the present clause is to identify the breakdown of a typical space system and to define a set of standard terms for the constituent levels within the breakdown (see Figure 21).
In so doing, it is acknowledged that each distinct domain (i.e. space, ground and launcher) already has its own domain-specific terminology for its internal entities e.g. elements and systems. In the case of the launcher domain, this terminology has been formally defined and agreed at programme-level. It is not the intention to define new terms in this Glossary to supersede those already in universal use. Rather, the intention is to define a standard set of terms for the levels of the space system breakdown and then to show where the domain-specific entities fit into these levels. To this end, Annex B contains examples of entities from the three principal space system segments, mapped to the space system breakdown levels defined below.
The terms are defined in clause 2.2.2 to 2.2.7 and are listed not in alphabetic order but according to the hierarchy defined in Figure 21: Space system breakdown below.
2.2.2 defines generic terms
2.2.3 defines the space system
2.2.4 defines terms relating to the space segment
2.2.5 defines terms relating to the ground segment
2.2.6 defines terms relating to the launch segment
2.2.7 defines terms relating to the support segment
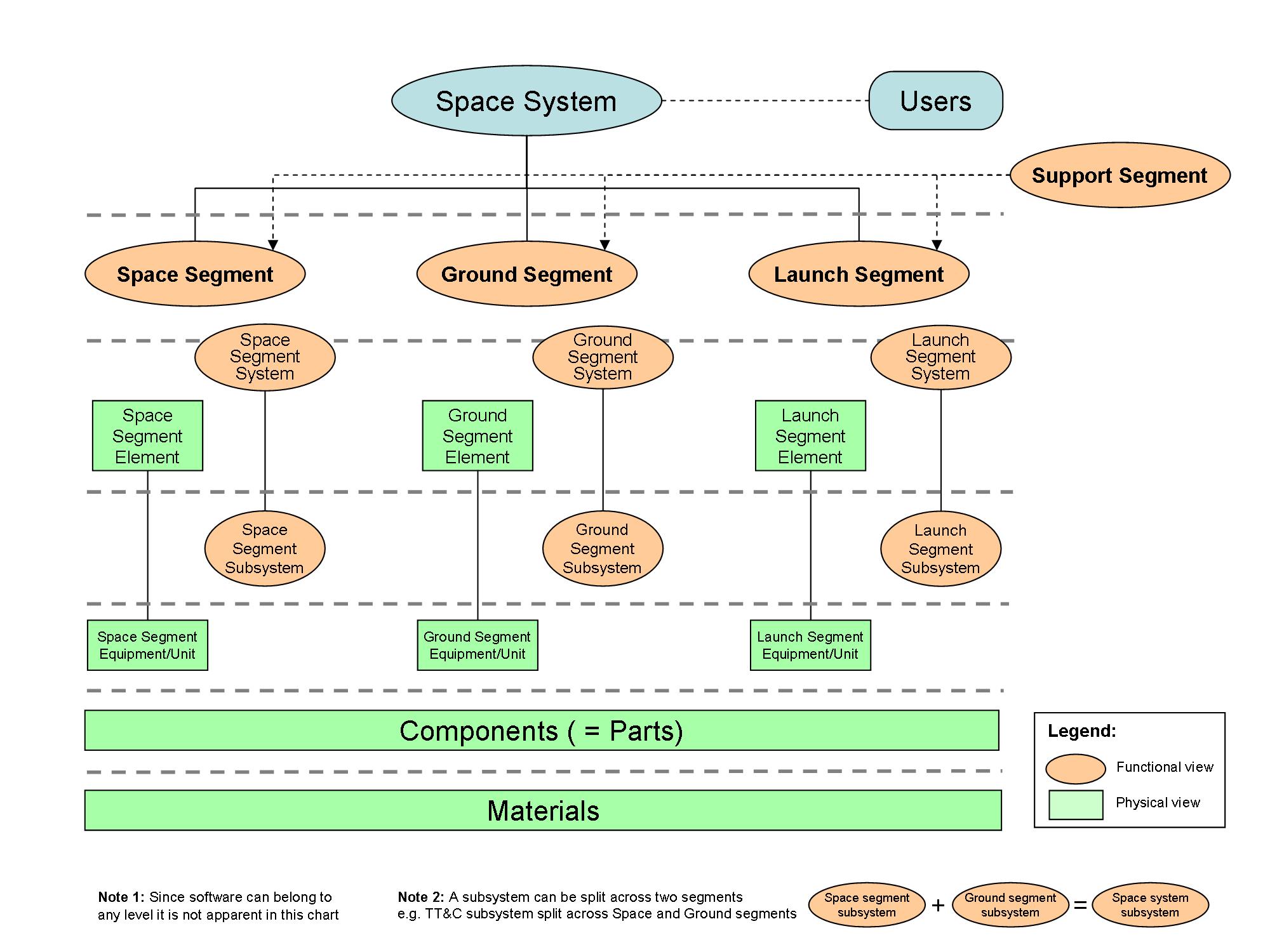 Figure 21: Space system breakdown
Figure 21: Space system breakdown
Definitions for generic terms
system
set of interrelated or interacting functions constituted to achieve a specified objective
segment
set of elements or combination of systems that fulfils a major, self-contained, subset of the space mission objectives
Examples are space segment, ground segment, launch segment and support segment.
element
combination of integrated equipment, components and parts
An element fulfils a major, self-contained, subset of a segment's objectives.
subsystem
part of a system fulfilling one or more of its functions
equipment
integrated set of parts and components
- 1 An equipment accomplishes a specific function.
- 2 An equipment is self-contained and classified as such for the purposes of separate manufacture, procurement, drawings, specification, storage, issue, maintenance or use.
- 3 The term "unit" is synonymous with the term "equipment"
component
set of materials, assembled according to defined and controlled processes, which cannot be disassembled without destroying its capability and which performs a simple function that can be evaluated against expected performance requirements
- 1 The term "part" is synonymous.
- 2 The term "part" is preferred when referring to purely mechanical devices.
- 3 The term "component" is preferred for EEE devices.
part
see "component"
material
raw, semi–finished or finished substance (gaseous, liquid, solid) of given characteristics from which processing into a component or part is undertaken
Definitions for space system
space system
system that contains at least a space, a ground or a launch segment
Generally a space system is composed of all three segments and is supported by a support segment.
Definitions for space segment
space segment
part of a space system, placed in space, to fulfil the space mission objectives
space segment system
system within a space segment
Examples are given in Annex B.1.
space segment element
element within a space segment
- 1 A space segment element can be composed of several space segment elements, e.g. a spacecraft is composed of instruments, a payload module and a service module.
- 2 Examples are given in Annex B.1.
stand-alone space segment element
space segment element that performs its mission autonomously
For example: satellite, rover, lander.
embedded space segment element
space segment element that performs its mission as part of another space segment element
For example: platform, module, instrument, payload.
space segment subsystem
subsystem within a space segment
Examples are given in Annex B.1.
space segment equipment
equipment within a space segment
Examples are given in Annex B.1.
Definitions for ground segment
ground segment
part of a space system, located on ground, which monitors and controls space segment element(s)
A ground segment is composed of one or more ground segment elements.
ground segment system
system within a ground segment
Examples are given in Annex B.2.
ground segment element
element within a ground segment
- 1 A ground segment element can be composed of several ground segment elements, e.g. a ground station network is a ground segment element that can be composed of a set of ground stations and a communication network.
- 2 Examples are given in Annex B.2.
ground segment subsystem
subsystem within a ground segment
Examples are given in Annex B.2.
ground segment equipment
equipment within a ground segment
Examples are given in Annex B.2.
Definitions for launch segment
launch segment
part of a space system which is used to transport space segment element(s) into space
- 1 A launch segment is composed of one or more launch segment elements.
- 2 A launch segment is composed of the integrated launcher and the facilities needed for manufacturing, testing and delivering launcher elements.
launch segment system
system within a launch segment
Examples are given in Annex B.3
launch segment element
element within a launch segment
- 1 A launch segment element can be composed of several launch segment elements, e.g. a launcher is a launch segment element that is composed of several launch segment elements, such as stage, engine and upper part.
- 2 Examples are given in Annex B.3.
launch segment subsystem
subsystem within a launch segment
Examples are given in Annex B.3.
launch segment equipment
equipment within a launch segment
Examples are given in Annex B.3.
Definitions for support segment
support segment
generic infrastructure and services used to support the development and operation of space system elements
- 1 Examples are ground stations and associated networks, orbit computing facilities, test centres, astronaut centre, launch facilities (e.g. Plestek, Baikonour, Guiana Space Centre).
- 2 Items can be part of other segments during their development and later become part of the support segment when used (e.g. a tracking network).
Terms and definitions
acceptance
<act> act by which the customer agrees that the product is designed and produced according to its specifications and the agreed deviations and waivers, and it is free of defects when delivered by the supplier
acceptance
<process> that part of the verification process which demonstrates that the product meets specified acceptance margins
accident
undesired event arising from operation of any project-specific item that results in
human death or injury,
loss of, or damage to, project hardware, software or facilities that can then affect the accomplishment of the mission,
loss of, or damage to, public or private property, or
detrimental effects on the environment.
Accident and mishap are synonymous.
active redundancy
redundancy where all entities are operating and the system can continue to operate without downtime or defects despite the loss of one or more entities
actuator
device that transforms an input signal into motion
alert
formal notification to users, informing them of failures or nonconformance of items, already released for use or not, which could also be present on other items already delivered [e.g. items with identical design concept, materials, components or processes]
An alert can also be raised when a deficiency in the specified requirements, which can affect the fitness for purpose in the defined application, has been identified.
allowable load
maximum load that can be permitted in a structural part for a given operating environment to prevent rupture, collapse, detrimental deformation or unacceptable crack growth
Adapted from ISO 14623:2003.
analysis
<verification> verification method utilizing techniques and tools to confirm that verification requirements have been satisfied
- 1 Examples of techniques and tools are mathematical models, compilation similarity assessments and validation of records.
- 2 Adapted from ISO 10795:2011.
anomaly
any deviation from the expected situation
An anomaly justifies an investigation that might lead to the discovery of a nonconformance or a defect.
applicable document
document that contains provisions which, through reference in the source document, constitute additional provisions of the source document
Adapted from ISO 10795:2011.
approval
formal agreement by a designated management official to use or apply an item or proceed with a proposed course of action
- 1 Approvals must be documented.
- 2 Approval implies that the approving authority has verified that the item conforms to its requirements.
assembly
<act> physically combining parts, components, equipment or segment elements to form a larger entity
assurance
planned and systematic activities implemented, and demonstrated as needed, to provide adequate confidence that an entity fulfils its requirements
audit
systematic, independent and documented process for obtaining audit evidence and evaluating it objectively to determine the extent to which audit criteria are fulfilled
- 1 Internal audits, sometimes called first-party audits, are conducted by, or on behalf of, the organization itself for management review and other internal purposes, and may form the basis for an organization’s declaration of conformity. In many cases, particularly in smaller organizations, independence can be demonstrated by the freedom from responsibility for the activity being audited.
- 2 External audits include those generally termed second- and third-party audits. Second-party audits are conducted by parties having an interest in the organization, such as customers, or by other persons on their behalf. Third-party audits are conducted by external, independent auditing organizations, such as those providing certification/registration of conformity to ISO 9001 or ISO 14001.
- 3 When quality and environmental management systems are audited together, this is termed “combined audit”.
- 4 When two or more auditing organizations cooperate to audit a single auditee jointly, this is termed “joint audit”.
[ISO 9000:2005]
audit criteria
set of policies, procedures or requirements
Audit criteria are used as a reference against which audit evidence is compared.
[ISO 9000:2005]
audit evidence
records, statements of fact or other information which are relevant to the audit criteria and verifiable
Audit evidence can be qualitative or quantitative.
[ISO 9000:2005]
auditee
organization being audited
[ISO 9000:2005]
auditor
person with the demonstrated personal attributes and competence to conduct an audit
Adapted from ISO 9000:2005.
availability
ability of an item to be in a state to perform a required function under given conditions at a given instant of time or over a given time interval, assuming that the required external resources are provided
- 1 This ability depends on the combined aspects of the reliability performance, the maintainability performance and the maintenance support performance.
- 2 Required external resources, other than maintenance resources do not affect the availability performance of the item.
- 3 When referring to the measure for availability, the preferred term is “instantaneous availability”.
- 4 Adapted from IEC Multilingual Dictionary: 2001 edition.
backward contamination
contamination of the terrestrial biosphere by extra-terrestrial life forms in the course of spaceflight missions
bakeout
activity of increasing the temperature of hardware to accelerate its outgassing rates with the intent of reducing the content of molecular contaminants within the hardware
Bakeout is usually performed in a vacuum environment, but may be done in a controlled atmosphere.
baseline
set of information which describes exhaustively a situation at a given instant of time or over a given time interval
A baseline is generally used as a reference for comparison with and analysis of subsequent evolutions of the information.
batch
quantity produced at one operation
black box
representation of an item whereby knowledge of its internal composition is not available to the user, only its function and interface characteristics are known
business agreement
legally binding agreement, for the supply of goods or services, between two or more actors in the customer–supplier chain
Business agreements are recorded in a variety of forms, such as:
- Contracts,
- Memoranda of understanding,
- Inter-governmental agreements,
- Inter-agency agreements,
- Partnerships,
- Bartering agreements, and
- Purchase orders.
calibration
all the operations for the purpose of determining the values of the errors and, if necessary, other metrological properties of a measuring instrument
The metrological use of the term “calibration” is often extended to include operations such as adjustments, scale graduation, etc. This use is deprecated.
[IEC Multilingual Dictionary: 2001 edition]
capability
ability of an organization, system or process to realize a product that will fulfil the requirements for that product
Process capability terms in the field of statistics are defined in ISO 3534-2.
[ISO 9000:2005]
catastrophic
<safety> resulting in loss of life, life-threatening, permanently disabling injury or occupational illness, loss of system, loss of an interfacing manned flight system, loss of launch site facilities or severe detrimental environmental effects
certification
procedure by which a party gives formal assurance that a person or an organization acts, or a product is, in compliance with specified requirements
Certification can be carried out by a first, second or third party.
clean area
area under contamination control
Examples of clean areas are cleanrooms, integration tent, gloves box.
cleanliness
level of particulate or molecular contamination
cleanroom
clean area controlled according to specified levels
Specified levels are humidity, temperature, particulates number versus size and volume and chemical contamination.
cold redundancy
redundancy where one entity is operating and the others are powered off
commissioning
verification and validation activities conducted after the launch and before the entry into operational service either on the space segment elements only or on the overall system (including the ground segment elements)
common cause failure
failure of multiple items occurring from a single cause that is common to all of them
common mode failure
failure of multiple identical items that fail in the same mode
Common mode failures are a particular case of common cause failures.
component
set of materials, assembled according to defined and controlled processes, which cannot be disassembled without destroying its capability and which performs a simple function that can be evaluated against expected performance requirements
-
1 The term "part" is synonymous.
-
2 The term "part" is preferred when referring to purely mechanical devices.
-
3 The term "component" is preferred for EEE devices.
composite
building block of a launcher composed of one or several pre-integrated stages and structural parts (fairing, payload adaptor, dual launch structure, etc.) -
1 Example-1: A5 Upper Composite includes the cryogenic upper stage (ESC), the vehicle equipment bay (VEB), fairing and payload adaptor.
-
2 Example-2: A5 Lower Composite includes two solid booster stages (EAP) and the main cryogenic stage (EPC).
configuration
interrelated functional and/or physical characteristics of a product defined in configuration documents subject to configuration management
Adapted from ISO 10007:2003.
configuration baseline
approved status of requirements and design of a product at a project key milestone that serves as a reference for activities throughout the life cycle of the product
Adapted from ISO 10007:2003.
configuration control
coordinated activities for controlling modifications to a configuration baseline
Requests for deviation are also considered modifications to a baseline.
configuration document
document that defines the requirements for function, design, build, production, and verification for a configuration item
For space standards, configuration documents can include documents relating to operation and disposal of the configuration item.
configuration identification
coordinated activities to establish rules for configuration item selection, configuration baseline content definition, and product and document identifiers definition
configuration item
aggregation of hardware, software, processed materials, services or any of its discrete portions, that is designated for configuration management and treated as a single entity in the configuration management process
A configuration item can contain other configuration item(s).
configuration management
activity for establishing and maintaining consistent records of the performance parameters of a product and its functional and physical attributes compared to product design and operational requirements
- 1 Configuration management is applied throughout the entire life cycle of the product (i.e. development, production, deployment, operation and disposal).
- 2 Adapted from ISO 10007:2003.
configuration status accounting
formalized recording and reporting of product characteristics and configuration information, the status of applicable changes and the status of their implementation
Adapted from ISO 10007:2003.
configuration verification
coordinated activities to determine the conformance of the configuration item to its configuration document(s)
conformance
fulfilment of a requirement
The term “conformity” is synonymous.
conformity
see “conformance”
* The term “conformance” is strongly recommended for use in the ECSS system.
contaminant
undesirable molecular or particulate matter
This includes microbiological matter.
contamination
introduction of contaminant to an item or to the environment of interest
contract
legally enforceable business agreement in which payment is part of the conditions
corrective action
action to eliminate the cause of a detected nonconformance, or other undesirable situation
- 1 There can be more than one cause for a non-conformance.
- 2 Corrective action is taken to prevent recurrence whereas preventive action is taken to prevent occurrence.
COTS
commercial electronic component readily available and not manufactured, inspected or tested in accordance with military or space standards
critical
<general> characteristic of a process, process condition, parameter, requirement or item that deserves control and special attention in order to meet the objectives (e.g. of a mission) within given constraints
critical
<safety> resulting in temporarily disabling but not life threatening injury, temporary occupational illness, major detrimental environmental effects, major damage to public or private properties, major damage to interfacing flight systems or major damage to ground facilities
critical item
potential threat to the schedule, cost, performance and quality of a project or programme that is controlled by a specific action plan in order to mitigate emanating risks and to prevent undesirable consequences
Examples of critical items are:
- item not qualified or validated for the application in question (or has caused problems previously which remained unresolved).
- item for which it is difficult to demonstrate design performance.
- item highly sensitive to the conditions under which it is produced or used (e.g. contamination, radiation).
- item having the potential to degrade the quality of the product significantly, and hence the ability of the end-product to accomplish defined mission objectives.
- item for which major difficulties or uncertainties are expected in the procurement, manufacturing, assembly, inspection, test, handling, storage and transportation, that have the potential to lead to a major degradation in the quality of the product.
critical path
chain of activities that determines the earliest completion of the project
As a consequence, any delay of one task belonging to the critical path extends the project duration.
customer
organization or person that receives a product as part of a business agreement
A customer can be internal or external to the supplier organization.
defect
non-fulfilment of a requirement related to an intended or specified use
-
1 The distinction between the concepts defect and nonconformance is important as it has legal connotations, particularly those associated with product liability issues. Consequently the term “defect” should be used with extreme caution.
-
2 The intended use as intended by the customer can be affected by the nature of the information, such as operating or maintenance instructions, provided by the supplier.
dependability
the extent to which the fulfilment of a required function can be justifiably trusted -
1 Its main components are reliability, availability and maintainability.
-
2 Dependability shall be considered in conjunction with safety.
derating
action when designing a product to limit the component stresses to specified levels that are below their ratings in order to increase its reliability
design
<result> set of information that defines the characteristics of a product
design
<activity> process used to generate the set of information defining the characteristics of a product
The design is completed at CDR closure.
development
complete process of elaborating a product from concept to manufacturing including its qualification and final acceptance
Technology development and design production are part of the process (i.e. from phase 0 to phase D).
deviation
formal authorization to depart from the originally specified requirements for a product, prior to its production
Waiver is an a posteriori decision whereas deviation is an a priori decision with respect to the production phase.
discipline
specific area of expertise within a general subject
The name of the discipline normally indicates the type of expertise (e.g. in the ECSS system, system engineering, mechanical engineering, software and communications are disciplines within the engineering domain).
discrepancy
departure from expected performance
- 1 A discrepancy can be the result of nonconforming hardware or software, or conditions occurring in test set-up.
- 2 A discrepancy can be momentary, non-repeatable, or permanent.
- 3 Adapted from ISO 10795:2011.
disposal
actions performed by a spacecraft or launch vehicle orbital stage to permanently reduce its chance of accidental break-up and to achieve its required long-term clearance of the protected regions
[ISO 24113:2011]
effectiveness
extent to which planned activities are realized and planned results achieved
[ISO 9000:2005]
efficiency
relationship between the result achieved and the resources used
[ISO 9000:2005]
element
combination of integrated equipment, components and parts
An element fulfils a major, self-contained, subset of a segment's objectives.
emergency
situation where hazardous events have occurred with potentially catastrophic or critical consequences requiring an immediate action
embedded space segment element
space segment element that performs its mission as part of another space segment element
For example: platform, module, instrument, payload.
end item
product that is deliverable under a business agreement
engineering model
flight representative model in terms of form, fit and function used for functional and failure effect verification
-
1 The engineering model is usually not equipped with high reliability parts or full redundancy.
-
2 The engineering model is also used for final validation of test facilities, GSE and associated procedures.
-
3 More detailed information on the build standard and the use of this model is given in ECSS-E-HB-10-02.
engineering qualification model
model, which fully reflects the design of the flight model except for the parts standard, used for functional performance and EMC verification and possibly for qualification -
1 Military grade or lower-level parts can be used instead of high reliability parts, provided they are procured from the same manufacturer with the same packaging.
-
2 Functional performance qualification includes verification of procedures for failure detection, isolation and recovery and for redundancy management.
-
3 The engineering qualification model may also be used for environmental testing if the customer accepts the risk, in which case the qualification model rules apply.
-
4 More detailed information on the build standard and the use of this model is given in ECSS-E-HB-10-02.
environment
natural conditions and induced conditions that constrain the design definitions or operations of a product -
1 Examples of natural conditions are weather, climate, ocean conditions, terrain, vegetation, dust, light and radiation.
-
2 Examples of induced conditions are electromagnetic interference, heat, vibration, pollution and contamination.
equipment
integrated set of parts and components -
1 An equipment accomplishes a specific function.
-
2 An equipment is self-contained and classified as such for the purposes of separate manufacture, procurement, drawings, specification, storage, issue, maintenance or use.
-
3 The term "unit" is synonymous with the term "equipment".
fail-safe
preventing the failure of an item from resulting in catastrophic or critical consequences
failure
the event resulting in an item being no longer able to perform its required function
"Failure" is an event, as distinguished from "fault" which is a state.
failure mode
mechanism through which a failure occurs
- 1 For example,. short-circuit, open-circuit, fracture, or excessive wear.
- 2 This term is equivalent to the term “fault mode” in IEC Multilingual Dictionary: 2001 edition.
failure tolerance
attribute of an item that makes it able to perform a required function in the presence of certain given sub-item failures
fault
state of an item characterized by inability to perform as required
- 1 A fault can be the result of a failure of the item itself or can exist without prior failure.
- 2 A fault can generate a failure.
fault tolerance
attribute of an item that makes it able to perform a required function in the presence of certain given sub-item faults
firmware
hardware that contains a computer program or data that cannot be changed in its user environment
The computer program and data contained in firmware are classified as software; the circuitry containing the computer program and data is classified as hardware.
flammability
measure of the ease with which a material is set on fire
flight model
end product that is intended for flight
- 1 The flight model is subjected to formal functional and environmental acceptance testing.
- 2 More detailed information on the build standard and the use of this model is given in ECSS-E-HB-10-02.
flight operations
all activities related to the planning, execution and evaluation of the control of the space segment when in orbit
flight spare
spare flight model that could be used in place of the flight model
- 1 Exceptionally, a refurbished qualification model can be used as a flight spare.
- 2 More detailed information on the build standard and the use of this model is given in ECSS-E-HB-10-02.
forward contamination
contamination of celestial bodies other than the Earth by terrestrial life forms in the course of spaceflight missions
function
intended effect of a product
function tree
hierarchical breakdown of a function into successive levels of function
functional analysis
process that describes completely the functions and their relationships, which are systematically characterised, classified and evaluated
ground segment
part of a space system, located on ground, which monitors and controls space segment element(s)
A ground segment is composed of one or more ground segment elements.
ground segment element
element within a ground segment
- 1 A ground segment element can be composed of several ground segment elements, e.g. a ground station network is a ground segment element that can be composed of a set of ground stations and a communication network.
- 2 Examples are given in Annex B.2.
ground segment equipment
equipment within a ground segment
Examples are given in Annex B.2.
ground segment subsystem
subsystem within a ground segment
Examples are given in Annex B.2.
ground segment system
system within a ground segment
Examples are given in Annex B.2.
ground support equipment
non flight product (hardware/software) used on ground to assemble, integrate, test, transport, access, handle, maintain, measure, calibrate, verify, protect or service a flight product (hardware/software)
handbook
<ECSS> non-normative document providing background information, orientation, advice or recommendations related to one specific discipline or to a specific technique, technology, process or activity
hazard
existing or potential condition that can result in a mishap
- 1 This condition can be associated with the design, manufacturing, operation or environment.
- 2 Hazards are not events but potential threats to safety.
hazardous event
mishap resulting from a hazard
hot redundancy
redundancy where all entities are powered on with only one operating
human factors
model of observed human physical and psycho-physiological behaviour in relation to environment and product
implementation document
formal response from the supplier to the customer’s Project Requirements Document describing how all requirements will be met
incident
unexpected event that might be, or could lead to, an operational interruption, disruption, loss, emergency, crisis or accident
Incidents are recorded for further assessment.
informative
providing non-normative information intended to assist the understanding or use of requirements
inhibit
<noun> design feature that prevents a function from undesirable execution
An inhibit can be software or hardware.
inspection
conformance evaluation by observation and judgement accompanied as appropriate by measurement, testing or gauging
[ISO 9000:2005]
integration
functionally combining lower-level functional entities (hardware or software) so they operate together to constitute a higher-level functional entity
Assembly is a pre-requisite for integration.
interchangeability
ability of a product to be used in place of another to fulfil the same requirements
interface
boundary where two or more products meet and interact
launch base
composed of launch range and launch complexes
launch campaign
launch activities which include:
Launcher preparation and final integration
Payload processing and integration on the launcher
Launch Operations including Flight Data Gathering
launch complex
integration and facilities necessary to carry out the final integration of the launcher elements as well as the launch operations
A Launch System is associated with its specific Launch Complex, which may include facilities shared with other Launch Systems (e.g.: Lox plant at CSG).
launch operations
all launch related activities taking place after completion of the activities necessary to deliver a fully integrated launcher up to reception of post flight data
launch range
systems, facilities and means, not part of the launch segment, required to provide the necessary service and support for carrying out a launch campaign and to ensure safety and security of persons, assets and protection of the environment
The Launch Range includes in particular the CNES/CSG technical centre, the payload Preparation Facilities as well as the downrange stations for launcher tracking and flight data acquisition.
launch segment
part of a space system which is used to transport space segment element(s) into space
-
1 A launch segment is composed of one or more launch segment elements.
-
2 A launch segment is composed of the integrated launcher and the facilities needed for manufacturing, testing and delivering launcher elements.
launch segment element
element within a launch segment -
1 A launch segment element can be composed of several launch segment elements, e.g. a launcher is a launch segment element that is composed of several launch segment elements, such as stage, engine and upper part.
-
2 Examples are given in Annex B.3.
launch segment equipment
equipment within a launch segment
Examples are given in Annex B.3.
launch segment subsystem
subsystem within a launch segment
Examples are given in Annex B.3.
launch segment system
system within a launch segment
Examples are given in Annex B.3
launch service
activities required to conclude a launch service contract and to place a payload in the orbit, at the time, and under the payload environment conditions required by the customer
Launch Service activities cover in particular: Commercialisation, Mission analysis, Procurement of a fully integrated launcher, Procurement of flight programme(s), Procurement of launcher adaptations to meet specific mission requirements, Payload processing and integration on the launcher, Launch Operations including Flight Data Gathering, Launch Range Operations, Post Flight Analysis.
launch system
system comprising the fully integrated launcher, the launch complex and the needed facilities for manufacturing, testing and delivering the launcher elements
"Fully integrated launcher" means the integrated launcher, including payload, and ready to be launched i.e. all launch control lights on green.
launch vehicle
see "launcher"
launcher
vehicle designed to transport payloads to space
The term “launch vehicle” is synonymous.
launcher element
building block of a launcher
[launcher] production facilities
launcher element manufacturing facilities and related launch complex
The launcher element manufacturing facilities include the test facilities specific to the launcher elements’ manufacturing.
launcher stage
complete element of a launcher that delivers the defined thrust during dedicated phase of the launcher mission
- 1 A launcher stage typically consists of a main propulsion system, a reaction controlled system (sometimes integrated to some extend with the main propulsion system), supporting structure, forward and aft skirts, aerodynamic control and/or stabilized surfaces, a separation system and a destruction system.
- 2 Some of the upper stages are also equipped with an avionics system.
- 3 The Ariane 5 upper stage is made of cryogenic main stage (ESC) and vehicle equipment bay (VEB).
launcher system
fully integrated launcher and the needed facilities for manufacturing, testing and delivering the launcher elements
"Fully integrated launcher" means the integrated launcher, including payload, and ready to be launched i.e. all launch control lights on green.
life cycle
all phases in the life of a product from needs identification through disposal
life profile
conditions to which a product is chronologically submitted from its manufacturing to its disposal
lifetime
period, or number of cycles, over which a product is required to perform according to its specification
lot
batch or portion of a batch
maintainability
ease of performing maintenance on a product
- Maintainability can be expressed as the probability that a maintenance action on a product can be carried out within a defined time interval, using stated procedures and resources.
maintenance
actions needed to retain a product in, or restore it to, a state in which it can perform its required function
Actions may include tuning, control, inspection, repair, replacement or redesign.
material
raw, semi–finished or finished substance (gaseous, liquid, solid) of given characteristics from which processing into a component or part is undertaken
mission
set of tasks, duties or functions to be accomplished by an element
model
physical or abstract representation used for calculations, predictions or further assessment
Model can also be used to identify particular instances of the product e.g. flight model.
multipaction
resonant back and forth flow of secondary electrons in a vacuum between two surfaces separated by a distance such that the electron transit time is an odd integral multiple of one half the period of the alternating voltage impressed on the surface
The effects of multipaction can be loss of output power up to reaching the multipaction breakdown voltage leading to the generation of spark.
nonconformance
non-fulfilment of a requirement
The term “nonconformity” is synonymous but deprecated.
nonconformity
see “nonconformance”
The term “nonconformity” is deprecated.
normative
providing requirements for activities or their results
- 1 A “normative document” covers documents such as standards, technical specifications, codes of practice and regulations.
- 2 A “normative reference" incorporates requirements from a cited publication into a normative document.
offgassing
outgassing under atmospheric or near-atmospheric pressure
Examples are manned and biological missions.
off-the-shelf
procured from the market, even if not developed for space application
orbital debris
see “space debris”
The term “orbital debris” is deprecated.
outage
state of a product being unable to perform its required function
outgassing
gaseous release from a material
Outgassing occurs in vacuum as well as in higher-pressure environments.
part
see "component"
payload
set of space segment elements
- 1 A spacecraft payload is a set of instruments or equipment which performs the user mission.
- 2 A launcher payload is a set of space segment elements carried into space in accordance with agreed position, time and environmental conditions.
performance
quantifiable characteristics of a function
planetary protection
policy and the technical implementations to prevent to prevent forward contamination and backward contamination
preventive action
action to eliminate the cause of a potential nonconformance or other undesirable potential situation
- 1 There can be more than one cause for a potential non-conformance.
- 2 Preventive action is taken to prevent occurrence whereas corrective action is taken to prevent recurrence.
procedure
documented way to carry out an activity or process in a controlled manner
process
set of interrelated or interacting activities which transform inputs into outputs
Inputs to a process are generally outputs of other processes.
product
result of a process
- 1 There are four generic product categories:
- services
- software
- hardware
- processed materials.
- 2 Adapted from ISO 9000:2005.
product assurance
discipline devoted to the study, planning and implementation of activities intended to assure that the design, controls, methods and techniques in a project result in a satisfactory degree of quality in a product
product tree
hierarchical breakdown of a product into successive levels of product
project
set of coordinated and controlled activities with start and finish dates, undertaken to achieve an objective conforming to specific requirements, including constraints of time, cost and resources
project requirements document
integral part of an ITT, RFP, or RFQ prepared and released by a customer to potential suppliers, addressing technical and programmatic requirements, as well as political, commercial, and industrial constraints
The response to a PRD is an ID.
protoflight model
flight model on which a partial or complete protoflight qualification test campaign is performed before flight
More detailed information on the build standard and the use of this model is given in ECSS-E-HB-10-02.
provision
expression in the content of a normative document, that takes the form of a statement, an instruction, a recommendation or a requirement
These types of provision are distinguished by the form of wording they employ, e.g. instructions are expressed in the imperative mood, recommendations by the use of the auxiliary “should” and requirements by the use of the auxiliary “shall”.
[EN 45020:2006]
qualification
that part of verification which demonstrates that the product meets specified qualification margins
This can apply to personnel, products, manufacturing and assembly processes.
qualification model
model, which fully reflects all aspects of the flight model design, used for complete functional and environmental qualification testing
- 1 A qualification model is only necessary for newly-designed hardware or when a delta qualification is performed for adaptation to the project.
- 2 The qualification model is not intended to be used for flight, since it is overtested.
- 3 More detailed information on the build standard and the use of this model is given in ECSS-E-HB-10-02.
quality
degree to which a set of characteristics of a product or process fulfils requirements
quality assurance
part of quality management focused on providing confidence that quality requirements will be fulfilled
[ISO 9000:2005]
quality control
part of quality management focused on fulfilling quality requirements
[ISO 9000:2005]
redundancy
existence of more than one means for performing a given function with the intention of increasing reliability
See also definitions for “active redundancy”, “hot redundancy” and “cold redundancy”.
reliability
the ability of an item to perform a required function under given conditions for a given time interval
- 1 It is generally assumed that the item is in a state to perform this required function at the beginning of the time interval.
- 2 Generally, reliability performance is quantified using appropriate measures. In some applications these measures include an expression of reliability performance as a probability, which is also called reliability.
relifing
quality control activity for the extension of the expiry datecode of a EEE component which is intended to be used for space application
repair
action to correct a defect of a product that leads to a configuration item change
- 1 Unlike rework, repair affects or modifies parts of the defective product.
- 2 An NCR needs to be raised for the CI change.
requirement
documented demand to be complied with
residual risk
risk remaining after implementation of risk reduction measures
[ISO 17666:2003]
review
activity undertaken to determine the suitability, adequacy and effectiveness of the subject matter to achieve established objectives
- 1 Review can also include the determination of efficiency.
- 2 Examples are: management review, design and development review, review of customer requirements and nonconformity review.
[ISO 9000:2005]
rework
action to correct a defect of a product that does not lead to a configuration item change
-
1 Unlike repair, rework does not affect or modify parts of the defective product.
-
2 No NCR needs to be raised.
risk
undesirable situation or circumstance that has both a likelihood of occurring and a potential negative consequence on a project -
1 Risks are inherent to any project, and can arise at any time during the project life cycle.
-
2 Predictability and control of events facilitate risk reduction.
-
3 The terms “risk assessment”, “risk mitigation” and “risk control” are in common use in ECSS.
-
4 Adapted from ISO 17666:2003.
safety
state where an acceptable level of risk is not exceeded
Risk relates to:
- fatality,
- injury or occupational illness,
- damage to launcher hardware or launch site facilities,
- damage to an element of an interfacing manned flight system,
- the main functions of a flight system itself,
- pollution of the environment, atmosphere or outer space, and
- damage to public or private property.
safety critical function
function that, if lost or degraded, or as a result of incorrect or inadvertent operation, can result in catastrophic or critical consequences
safing
action of containment or control of emergency and warning situations, or placing a system (or part thereof), in a predetermined safe condition
scrap
action on a nonconforming product to preclude its originally intended use
- 1 The scrapped product is not recoverable by rework or repair for technical or economic reasons. As a consequence, it will be recycled or destroyed.
- 2 A service is scrapped by being discontinued.
security
state where an acceptable level of risk arising from malevolent action is not exceeded
segment
set of elements or combination of systems that fulfils a major, self-contained, subset of the space mission objectives
Examples are space segment, ground segment, launch segment and support segment.
severity
classification of a failure or undesired event according to the magnitude of its possible consequences
single point failure
part of a product that, if it fails, will result in the unrecoverable failure of that product
solar array
assembly of solar panels on a supporting structure with associated hardware
The associated hardware includes mounting features, cables and, in the case of a deployable solar array, a deployment mechanism.
solar cell
photovoltaic component that converts solar radiation to electricity
solar cell assembly
solar cell together with interconnector, coverglass and, if used, by-pass diode
solar panel
interconnected solar cell assemblies mounted on a substrate
space debris
non-functional fragments of, or residue from, a space segment element, or launch segment element, in Earth orbit or re-entering the Earth’s atmosphere
The term “orbital debris” is synonymous, but deprecated.
space mission
user-defined mission to be achieved by a space system
space programme
set of related space projects managed in a coordinated way to contribute to an overall objective
space segment
part of a space system, placed in space, to fulfil the space mission objectives
space segment element
element within a space segment
- 1 A space segment element can be composed of several space segment elements, e.g. a spacecraft is composed of instruments, a payload module and a service module.
- 2 Examples are given in Annex B.1.
space segment equipment
equipment within a space segment
Examples are given in Annex B.1.
space segment subsystem
subsystem within a space segment
Examples are given in Annex B.1.
space segment system
system within a space segment
Examples are given in Annex B.1.
space system
system that contains at least a space, a ground or a launch segment
Generally a space system is composed of all three segments and is supported by a support segment.
spacecraft
manned or unmanned vehicle designed to orbit or travel in space
A spacecraft is a space segment element.
special process
process where the quality cannot be completely ensured by inspection of the end article only
specification
document stating requirements
A specification can be related to activities (e.g. procedure document, process specification and test specification), or products (e.g. product specification, performance specification and drawing).
[ISO 9000:2005]
stand-alone space segment element
space segment element that performs its mission autonomously
For example: satellite, rover, lander.
standard
<ECSS> normative document for use in invitations to tender and business agreements for implementing space related activities
- 1 A standard states verifiable requirements, supported by the minimum descriptive text necessary to understand their context. Each requirement has a unique identification, allowing full traceability and easy verification of compliance.
- 2 A standard is established by consensus amongst all ECSS stakeholders.
- 3 Other Standards Development Organisations (SDOs) use a different definition.
statement of work
contractual document that describes and plans deliverables and activities required to complete a project
The statement of work is issued by the customer at the start of a project for implementation by the supplier.
stress-corrosion
combined action of sustained tensile stress and corrosion that can lead to premature failure of materials
structural model
structurally representative model of the flight model used for qualification of the structural design and for correlation with structural mathematical models
- 1 The system structural model usually consists of a representative structure, with structural dummies of the flight equipment, and also includes representative mechanical parts of other subsystems (e.g. mechanisms and solar panels).
- 2 The system structural model is also used for final validation of test facilities, GSE, and associated procedures.
- 3 More detailed information on the build standard and the use of this model is given in ECSS-E-HB-10-02.
structuralthermal model
structurally and thermally representative model of the flight model that combines the objectives of the structural model and the thermal model
More detailed information on the build standard and the use of this model is given in ECSS-E-HB-10-02.
subsystem
part of a system fulfilling one or more of its functions
supplier
organization or person that provides a product as part of a business agreement
A supplier can be internal or external to the customer organization.
support segment
generic infrastructure and services used to support the development and operation of space system elements
- 1 Examples are ground stations and associated networks, orbit computing facilities, test centres, astronaut centre, launch facilities (e.g. Plestek, Baikonour, Guiana Space Centre).
- 2 Items can be part of other segments during their development and later become part of the support segment when used (e.g. a tracking network).
support system
see "support segment"
The term "support system" is deprecated.
system
set of interrelated or interacting functions constituted to achieve a specified objective
tailoring
process by which standards are made applicable to a specific project by selection of existing requirements, with or without modification, or addition of new ones
technical memorandum
<ECSS> non-normative document providing useful information to the space community on a specific subject
Technical Memoranda are prepared to record and present data which are not the subject for a standard or for a handbook or not yet mature enough to be published as standard or handbook.
test
measurement of product characteristics, performance or functions under representative environments
thermal ambient test
test conducted at ambient pressure and under predefined temperature conditions to demonstrate the capability of the test item to operate according to requirements
- 1 Temperature conditions can be expressed as temperature level, gradient and variation.
- 2 The ambient pressure can be mission dependent.
thermal balance test
test conducted under steady state conditions to correlate and adjust the thermal mathematical model and verify the thermal design
thermal model
thermally representative model of the flight model used for verification of the thermal design and for correlation with thermal mathematical models
- 1 The system thermal model usually consists of a representative structure, with thermal dummies of the flight equipment, and also includes representative thermal parts of other subsystems.
- 2 More detailed information on the build standard and the use of this model is given in ECSS-E-HB-10-02.
thermal vacuum test
test conducted in vacuum under predefined temperature conditions to demonstrate the capability of the test item to operate according to requirements
Temperature conditions can be expressed as temperature level, gradient and variation.
third party
person or body that is recognized as being independent of the parties involved, as concerns the issue in question
Parties involved are usually supplier (“first party”) and purchaser (“second party”).
[EN 45020:1998]
toxic
characteristic of a substance causing serious, acute or chronic effects, even death, when inhaled, swallowed or absorbed through the skin
traceability
ability to track the history, location or application by means of documented records
When considering a product, traceability can relate to:
- the origin of materials and parts,
- the processing history, or
- the distribution and location of the product after delivery.
uncertainty
lack of certitude resulting from inaccuracies of input parameters, analysis process, or both
unit
see "equipment"
The term “equipment” is strongly recommended for use in the ECSS system.
upper part [A5]
made of all the payload adaptor's (ACU), SYLDA or Speltra and Fairing [Ariane 5 launcher]
upper stage [A5]
made of cryogenic main stage (ESC) and vehicle equipment bay (VEB), ending at 1780 diameter interface [Ariane 5 launcher]
validation
process which demonstrates that the product is able to accomplish its intended use in the intended operational environment
-
1 The status of the product following validation is “validated”.
-
2 Verification is a pre-requisite for validation.
verification
process which demonstrates through the provision of objective evidence that the product is designed and produced according to its specifications and the agreed deviations and waivers, and is free of defects -
1 A waiver can arise as an output of the verification process.
-
2 Verification can be accomplished by one or more of the following methods: analysis (including similarity), test, inspection, review of design.
-
3 The status of the product following verification is “verified”.
waiver
formal authorization to accept products which during production, or after having been submitted to inspection or tests, are found to depart from specified requirements -
1 Deviation is an a priori decision whereas waiver is an a posteriori decision with respect to the production phase.
-
2 The term “concession” is synonymous and may be used for materials as per Q-ST-70C.
work breakdown structure
hierarchical representation of the activities necessary to complete a project
work package
group of related tasks that are defined down to the lowest level within a work breakdown structure
Abbreviated terms
|
Abbreviation
|
Meaning
|
|
A/D
|
analogue-to-digital
|
|
ABM
|
apogee boost motor
|
|
AC
|
alternating current
|
|
ADC
|
analogue-to-digital converter
|
|
AIT
|
assembly, integration and test
|
|
AIV
|
assembly, integration and verification
|
|
AOCS
|
attitude and orbit control subsystem
|
|
APS
|
active pixel sensor
|
|
AQL
|
acceptance quality level
|
|
AR
|
acceptance review
|
|
ASIC
|
application specific integrated circuit
|
|
ASTM
|
American Society for Testing and Materials
|
|
ATOX
|
atomic oxygen
|
|
AWG
|
American wire gauge
|
|
BOL
|
beginning-of-life
|
|
CAD
|
computer aided design
|
|
CCB
|
configuration control board
|
|
CCD
|
charge coupled device
|
|
CCSDS
|
Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems
|
|
CDR
|
critical design review
|
|
CIDL
|
configuration item data list
|
|
CIL
|
critical items list
|
|
CoG
|
centre of gravity
|
|
CoM
|
centre of mass
|
|
COTS
|
commercial off-the-shelf
|
|
CVCM
|
collected volatile condensable material
|
|
DC
|
direct current
|
|
DDF
|
design definition file
|
|
DDR
|
detailed design review
|
|
DJF
|
design justification file
|
|
DML
|
declared materials list
|
|
DMPL
|
declared mechanical parts list
|
|
DPL
|
declared processes list
|
|
DRB
|
delivery review board
|
|
DRD
|
document requirements definition
|
|
DRL
|
document requirements list
|
|
ECLS
|
environmental control and life support
|
|
ECSS
|
European Cooperation for Space Standardization
|
|
EED
|
electro-explosive device
|
|
EEE
|
electrical, electronic and electromechanical
|
|
EGSE
|
electrical ground support equipment
|
|
EIDP
|
end item data package
|
|
ELR
|
end-of-life review
|
|
EM
|
engineering model
|
|
EMC
|
electromagnetic compatibility
|
|
EMI
|
electromagnetic interference
|
|
EN
|
European Standard
|
|
EOL
|
end-of-life
|
|
ESA
|
European Space Agency
|
|
ESCC
|
European Space Components Coordination
|
|
ESD
|
electrostatic discharge
|
|
FDIR
|
failure detection isolation and recovery
|
|
FM
|
flight model
|
|
FMEA
|
failure modes and effects analysis
|
|
FMECA
|
failure modes, effects and criticality analysis
|
|
FOS
|
factor of safety
|
|
FRR
|
flight readiness review
|
|
FTA
|
fault tree analysis
|
|
GEO
|
geostationary orbit
|
|
GS
|
ground segment
|
|
GSE
|
ground support equipment
|
|
HMI
|
human-machine interface
|
|
HSIA
|
hardware-software interaction analysis
|
|
HW
|
hardware
|
|
ICD
|
interface control document
|
|
ILS
|
integrated logistic support
|
|
IRD
|
interface requirements document
|
|
ISO
|
International Organization for Standardization
|
|
ISS
|
International Space Station
|
|
I/F
|
interface
|
|
I/O
|
input/output
|
|
LEO
|
low Earth orbit
|
|
LEOP
|
launch and early orbit phase
|
|
LRR
|
launch readiness review
|
|
MCR
|
mission close-out review
|
|
MDD
|
mission description document
|
|
MDP
|
maximum design pressure
|
|
MDR
|
mission definition review
|
|
MEOP
|
maximum expected operating pressure
|
|
MGSE
|
mechanical ground support equipment
|
|
MIP
|
mandatory inspection point
|
|
MLI
|
multi-layer insulation
|
|
MMIC
|
monolithic microwave integrated circuit
|
|
MOI
|
moment of inertia
|
|
NASA
|
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
|
|
NCR
|
nonconformance report
|
|
NDI
|
non-destructive inspection
|
|
NDT
|
non-destructive test
|
|
NRB
|
nonconformance review board
|
|
N/A
|
not applicable
|
|
OBDH
|
on-board data handling
|
|
ORR
|
operational readiness review
|
|
OTS
|
off-the-shelf
|
|
PA
|
product assurance
|
|
PCB
|
printed circuit board
|
|
PDR
|
preliminary design review
|
|
PFM
|
protoflight model
|
|
PID
|
process identification document
|
|
PMP
|
parts, materials and processes
|
|
PRR
|
preliminary requirements review
|
|
PTR
|
post test review
|
|
QA
|
quality assurance
|
|
QM
|
qualification model
|
|
QR
|
qualification review
|
|
RAMS
|
reliability, availability, maintainability and safety
|
|
RB
|
requirements baseline
|
|
RF
|
radio frequency
|
|
RFA
|
request for approval
|
|
RFD
|
request for deviation
|
|
RFW
|
request for waiver
|
|
RH
|
relative humidity
|
|
RID
|
review item discrepancy
|
|
ROD
|
review of design
|
|
r.m.s.
|
root-mean-square
|
|
SCC
|
stress-corrosion cracking
|
|
SEE
|
single event effect
|
|
SEP
|
system engineering plan
|
|
SRR
|
system requirements review
|
|
STM
|
structural-thermal model
|
|
SVT
|
system validation test
|
|
S/C
|
spacecraft
|
|
SW
|
software
|
|
TC
|
telecommand
|
|
TCS
|
thermal control subsystem
|
|
TM
|
telemetry
|
|
TM/TC
|
telemetry/telecommand
|
|
TML
|
total mass loss
|
|
TRB
|
test review board
|
|
TRL
|
technology readiness level
|
|
TRR
|
test readiness review
|
|
TS
|
technical specification
|
|
TT&C
|
telemetry, tracking and command
|
|
UTC
|
coordinated universal time
|
|
UV
|
ultraviolet
|
|
VCD
|
verification control document
|
|
VP
|
verification plan
|
|
WBS
|
work breakdown structure
|
ANNEXTraceability with respect to ECSS-P-001B
The following table shows the differences between ECSS-P-001B and this document.
Deleted terms (terms that appeared in ECSS-P-001B but do not appear in the current document) are listed after this table.
|
Term
|
Type of modification
|
|
2.3.1 acceptance <act>
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.2 acceptance <process>
|
Added
|
|
2.3.3 accident
|
No change
|
|
2.3.4 active redundancy
|
Added
|
|
2.3.5 actuator
|
Added
|
|
2.3.6 alert
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.7 allowable load
|
No change
|
|
2.3.8 analysis
|
Added
|
|
2.3.9 anomaly
|
No change
|
|
2.3.10 applicable document
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.11 approval
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.12 assembly <act>
|
Added
|
|
2.3.13 assurance
|
No change
|
|
2.3.14 audit
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.15 audit criteria
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.16 audit evidence
|
No change
|
|
2.3.17 auditee
|
No change
|
|
2.3.18 auditor
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.19 availability
|
No change
|
|
2.3.20 backward contamination
|
Added
|
|
2.3.21 bakeout
|
No change
|
|
2.3.22 baseline
|
No change
|
|
2.3.23 batch
|
Added
|
|
2.3.24 black box
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.25 business agreement
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.26 calibration
|
No change
|
|
2.3.27 capability
|
No change
|
|
2.3.28 catastrophic
|
Added
|
|
2.3.29 certification
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.30 clean area
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.31 cleanliness
|
Added
|
|
2.3.32� cleanroom
|
Added
|
|
2.3.33 cold redundancy
|
Added
|
|
2.3.34 commissioning
|
Added
|
|
2.3.35 common cause failure
|
No change
|
|
2.3.36 common mode failure
|
No change
|
|
2.3.37 component
|
Added
|
|
2.3.38 composite
|
Added
|
|
2.3.39 configuration
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.40 configuration baseline
|
No change
|
|
2.3.41 configuration control
|
No change
|
|
2.3.42 configuration document
|
No change
|
|
2.3.43 configuration identification
|
No change
|
|
2.3.44 configuration item
|
No change
|
|
2.3.45 configuration management
|
No change
|
|
2.3.46 configuration status accounting
|
No change
|
|
2.3.47 configuration verification
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.48 conformance
|
Added
|
|
2.3.49 conformity
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.50 contaminant
|
Added
|
|
2.3.51 contamination
|
No change
|
|
2.3.52 contract
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.53 corrective action
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.54 COTS
|
Added
|
|
2.3.55 critical <general>
|
Added
|
|
2.3.56 critical <safety>
|
Added
|
|
2.3.57 critical item
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.58 critical path
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.59 customer
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.60 defect
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.61 dependability
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.62 derating
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.63 design <result>
|
No change
|
|
2.3.64 design <activity>
|
No change
|
|
2.3.65 development
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.66 deviation
|
Added
|
|
2.3.67 discipline
|
Added
|
|
2.3.68 discrepancy
|
Added
|
|
2.3.69 disposal
|
Added
|
|
2.3.70 effectiveness
|
No change
|
|
2.3.71 efficiency
|
No change
|
|
2.3.72 element
|
Added
|
|
2.3.73 emergency
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.74 embedded space segment element
|
Added
|
|
2.3.75 end item
|
Added
|
|
2.3.76 engineering model
|
Added
|
|
2.3.77 engineering qualification model
|
Added
|
|
2.3.78 environment
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.79 equipment
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.80 fail-safe
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.81 failure
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.82 failure mode
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.83 failure tolerance
|
No change
|
|
2.3.84 fault
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.85 fault tolerance
|
No change
|
|
2.3.86 firmware
|
No change
|
|
2.3.87 flammability
|
No change
|
|
2.3.88 flight model
|
Added
|
|
2.3.89 flight operations
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.90 flight spare
|
Added
|
|
2.3.91 forward contamination
|
Added
|
|
2.3.92 function
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.93 function tree
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.94 functional analysis
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.95 ground segment
|
Added
|
|
2.3.96 ground segment element
|
Added
|
|
2.3.97 ground segment equipment
|
Added
|
|
2.3.98 ground segment subsystem
|
Added
|
|
2.3.99 ground segment system
|
Added
|
|
2.3.100 ground support equipment
|
Added
|
|
2.3.101 handbook <ECSS>
|
Added
|
|
2.3.102 hazard
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.103 hazardous event
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.104 hot redundancy
|
Added
|
|
2.3.105 human factors
|
Added
|
|
2.3.106 implementation document
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.107 incident
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.108 informative
|
Added
|
|
2.3.109 inhibit
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.110 inspection
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.111 integration
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.112 interchangeability
|
Added
|
|
2.3.113 interface
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.114 launch base
|
Added
|
|
2.3.115 launch campaign
|
Added
|
|
2.3.116 launch complex
|
Added
|
|
2.3.117 launch operations
|
Added
|
|
2.3.118 launch range
|
Added
|
|
2.3.119 launch segment
|
Added
|
|
2.3.120 launch segment element
|
Added
|
|
2.3.121 launch segment equipment
|
Added
|
|
2.3.122 launch segment subsystem
|
Added
|
|
2.3.123 launch segment system
|
Added
|
|
2.3.124 launch service
|
Added
|
|
2.3.125 launch system
|
Added
|
|
2.3.126 launch vehicle
|
Added
|
|
2.3.127 launcher
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.128 launcher element
|
Added
|
|
2.3.129 [launcher] production facilities
|
Added
|
|
2.3.130 launcher stage
|
Added
|
|
2.3.131 launcher system
|
Added
|
|
2.3.132 life cycle
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.133 life profile
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.134 lifetime
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.135 lot
|
Added
|
|
2.3.136 maintainability
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.137 maintenance
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.138 material
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.139 mission
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.140 model
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.141 multipaction
|
Added
|
|
2.3.142 nonconformance
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.143 nonconformity
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.144 normative
|
Added
|
|
2.3.145 offgassing
|
Added
|
|
2.3.146 off-the-shelf
|
Added
|
|
2.3.147 orbital debris
|
Added
|
|
2.3.148 outage
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.149 outgassing
|
Added
|
|
2.3.150 part
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.151 payload
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.152 performance
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.153 planetary protection
|
Added
|
|
2.3.154 preventive action
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.155 procedure
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.156 process
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.157 product
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.158 product assurance
|
No change
|
|
2.3.159 product tree
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.160 project
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.161 project requirements document
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.162 protoflight model
|
Added
|
|
2.3.163 provision
|
No change
|
|
2.3.164 qualification
|
Added
|
|
2.3.165 qualification model
|
Added
|
|
2.3.166 quality
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.167 quality assurance
|
No change
|
|
2.3.168 quality control
|
No change
|
|
2.3.169 redundancy
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.170 reliability
|
No change
|
|
2.3.171 relifing
|
Added
|
|
2.3.172 repair
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.173 requirement
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.174 residual risk
|
No change
|
|
2.3.175 review
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.176 rework
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.177 risk
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.178 safety
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.179 safety critical function
|
No change
|
|
2.3.180 safing
|
No change
|
|
2.3.181 scrap
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.182 security
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.183 segment
|
Added
|
|
2.3.184 severity
|
No change
|
|
2.3.185 single point failure
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.186 solar array
|
Added
|
|
2.3.187 solar cell
|
Added
|
|
2.3.188 solar cell assembly
|
Added
|
|
2.3.189 solar panel
|
Added
|
|
2.3.190 space debris
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.191 space mission
|
Added
|
|
2.3.192 space programme
|
Added
|
|
2.3.193 space segment
|
Added
|
|
2.3.194 space segment element
|
Added
|
|
2.3.195 space segment equipment
|
Added
|
|
2.3.196 space segment subsystem
|
Added
|
|
2.3.197 space segment system
|
Added
|
|
2.3.198 space system
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.199 spacecraft
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.200 special process
|
Added
|
|
2.3.201 specification
|
No change
|
|
2.3.202 stand-alone space segment element
|
Added
|
|
2.3.203 standard <ECSS>
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.204 statement of work
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.205 stress-corrosion
|
No change
|
|
2.3.206 structural model
|
Added
|
|
2.3.207 structuralthermal model
|
Added
|
|
2.3.208 subsystem
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.209 supplier
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.210 support segment
|
Added
|
|
2.3.211 support system
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.212 system
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.213 tailoring
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.214 technical memorandum <ECSS>
|
Added
|
|
2.3.215 test
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.216 thermal ambient test
|
Added
|
|
2.3.217 thermal balance test
|
Added
|
|
2.3.218 thermal model
|
Added
|
|
2.3.219 thermal vacuum test
|
Added
|
|
2.3.220 third party
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.221 toxic
|
No change
|
|
2.3.222 traceability
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.223 uncertainty
|
No change
|
|
2.3.224 unit
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.225 upper part [A5]
|
Added
|
|
2.3.226 upper stage [A5]
|
Added
|
|
2.3.227 validation
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.228 verification
|
Modified
|
|
2.3.229 waiver
|
Added
|
|
2.3.230 work breakdown structure
|
No change
|
|
2.3.231 work package
|
Modified
|
Terms deleted with respect to the previous issue of the glossary (ECSS-P-001B):
acceptance stage
acceptance test
allowable stress
assembly <noun>
audit client
audit conclusion
audit findings
audit programme
audit team
caution condition
characteristic
common mode fault
competence
concession
constraint
contingency procedure
continual improvement
contractor
correction
corrosion
cost breakdown structure
customer satisfaction
design and development
design to minimum risk
deviation permit
document
EEE component
error
estimate at completion
estimate to completion
fault <event>
flashpoint
grade
ground operations
ground systems
human error
information
infrastructure
instantaneous availability
integrity
item
life cycle cost
management
management system
matériel
mean time between failures
measurement control system
measurement process
measuring equipment
mechanical part
metrological characteristic
metrological confirmation
metrological function
need
normative document
normative reference
objective evidence
organization
organizational structure
product state
programme
project phase
purchaser
qualification process
quality characteristic
quality improvement
quality manual
quality plan
quality planning
record
recurrent cost
regrade
required function
risk management
risk management policy
series production
software module
software product
software product assurance
space element
space project
subcontract
supported system
technical expert
technical specification
top management
undesirable event
warning condition
work environment
ANNEXSegment trees
This annex includes example for the terms defined in paragraph 2.1 and Figure 21: Space system breakdown:
Space segment
Ground segment
Launch segment
Support segment
Space segment
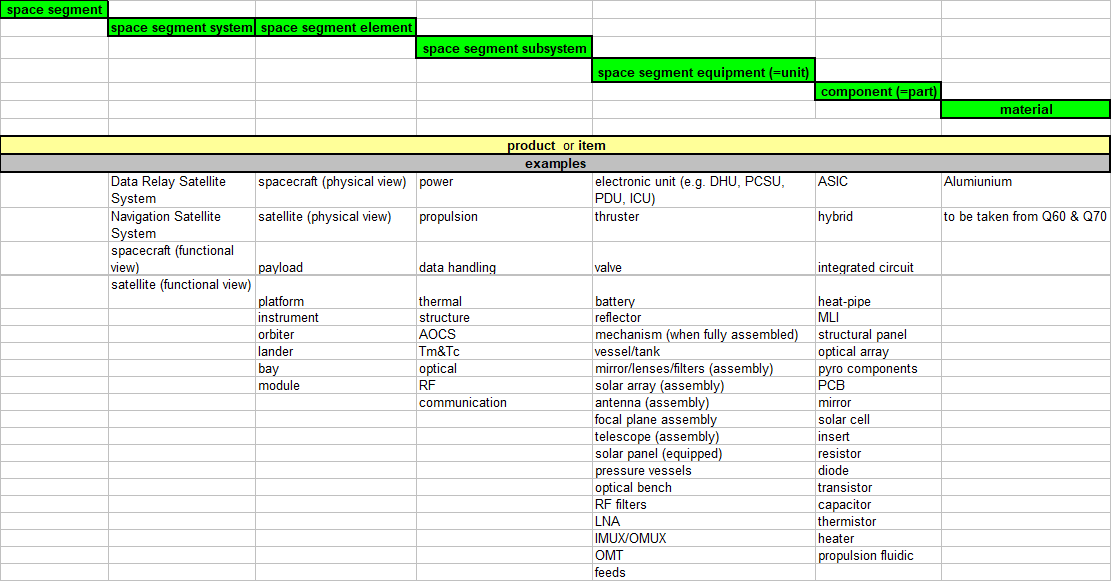
Ground segment
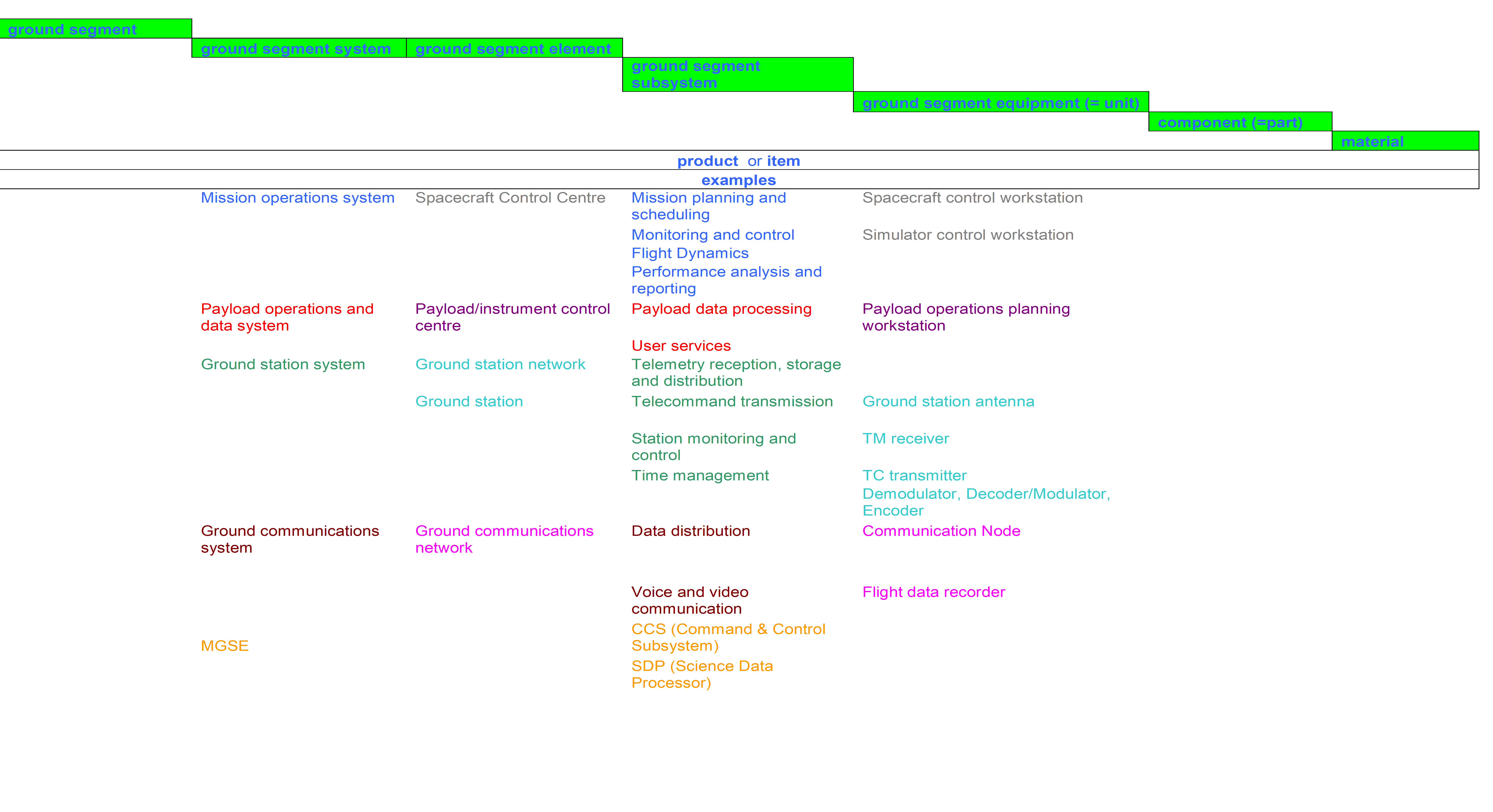
Launch segment
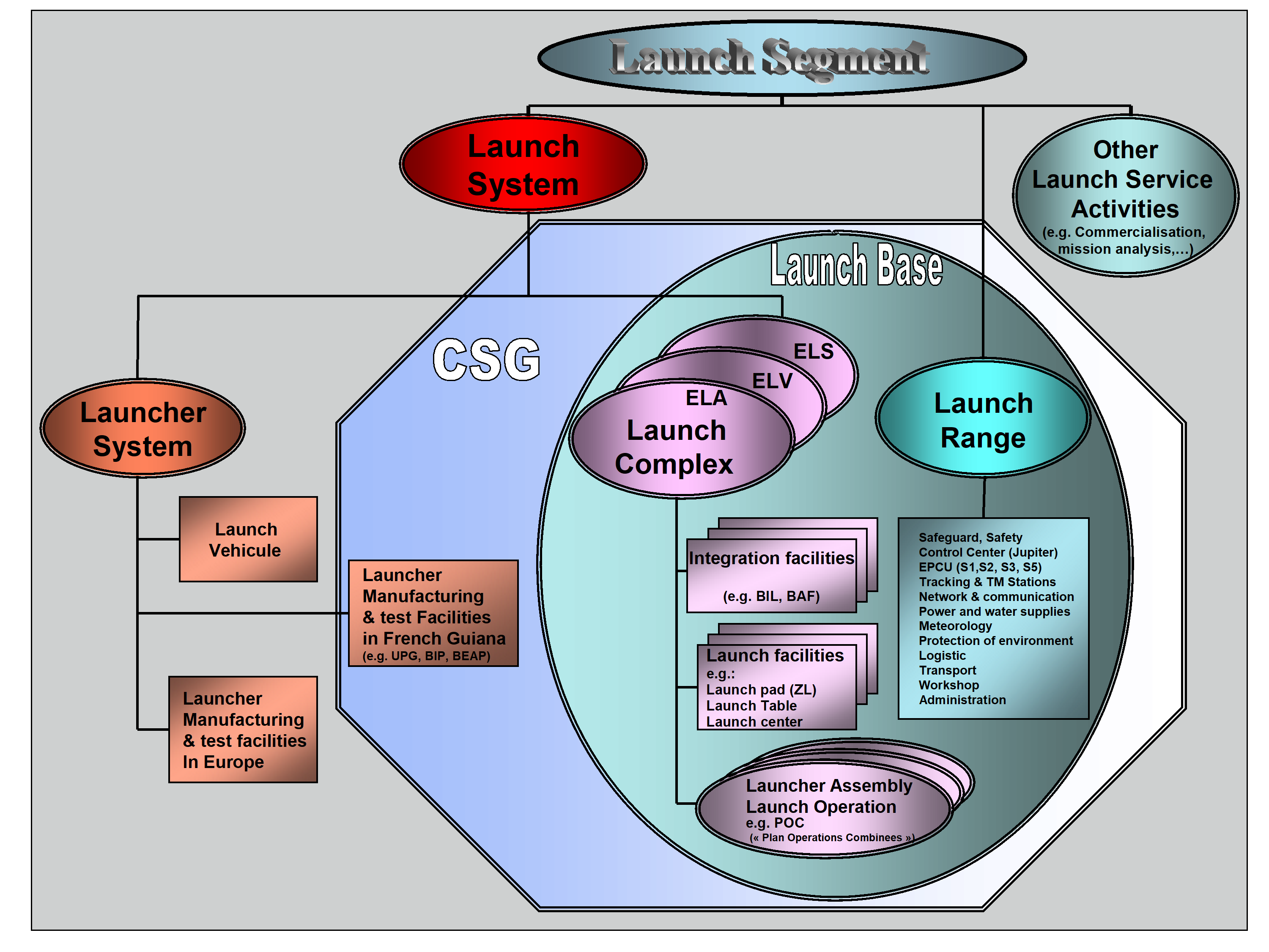
Support segment
|
Systems
|
|
Elements
|
|
|
Examples
|
|
|
Data Relay Satellite System
|
|
Data Relay Satellite
|
|
Navigation Satellite System
|
|
ISS
|
|
Concurrent Design Facility (CDF)
|
|
Astronaut training centre
|
|
Generic Flight Dynamics system (e.g. ORATOS)
|
|
Ground Statin Network Control Centre
|
|
|
|
Main Control room
|
|
LEOP Ground Station Network
|
|
Briefing Room
|
|
Deep Space Ground Station Network
|
|
Test Centre
|
|
|
|
MGSE
|
|
|
|
TGSE
|
|
|
|
FGSE
|
|
|
|
Launch complex
|
ANNEXLaunch segment-specific terms
The following terms are specific to the launcher domain and are cross-referenced from clause 2.3.
composite
building block of a launcher composed of one or several pre-integrated stages and structural parts (fairing, payload adaptor, dual launch structure, etc.)
- 1 Example-1: A5 Upper Composite includes the cryogenic upper stage (ESC), the vehicle equipment bay (VEB), fairing and payload adaptor.
- 2 Example-2: A5 Lower Composite includes two solid booster stages (EAP) and the main cryogenic stage (EPC).
launch base
composed of launch range and launch complexes
launch campaign
launch activities which include:
Launcher preparation and final integration
Payload processing and integration on the launcher
Launch Operations including Flight Data Gathering
launch complex
integration and facilities necessary to carry out the final integration of the launcher elements as well as the launch operations
A Launch System is associated with its specific Launch Complex, which may include facilities shared with other Launch Systems (e.g.: Lox plant at CSG).
launch operations
all launch related activities taking place after completion of the activities necessary to deliver a fully integrated launcher up to reception of post flight data
launch range
systems, facilities and means, not part of the launch segment, required to provide the necessary service and support for carrying out a launch campaign and to ensure safety and security of persons, assets and protection of the environment
The Launch Range includes in particular the CNES/CSG technical centre, the payload Preparation Facilities as well as the downrange stations for launcher tracking and flight data acquisition.
launch service
activities required to conclude a launch service contract and to place a payload in the orbit, at the time, and under the payload environment conditions required by the customer
Launch Service activities cover in particular: Commercialisation, Mission analysis, Procurement of a fully integrated launcher, Procurement of flight programme(s), Procurement of launcher adaptations to meet specific mission requirements, Payload processing and integration on the launcher, Launch Operations including Flight Data Gathering, Launch Range Operations, Post Flight Analysis.
launch system
system comprising the fully integrated launcher, the launch complex and the needed facilities for manufacturing, testing and delivering the launcher elements
"Fully integrated launcher" means the integrated launcher, including payload, and ready to be launched i.e. all launch control lights on green.
launch vehicle
see "launcher"
launcher
vehicle designed to transport payloads to space
The term “launch vehicle” is synonymous.
launcher element
building block of a launcher
[launcher] production facilities
launcher element manufacturing facilities and related launch complex
The launcher element manufacturing facilities include the test facilities specific to the launcher elements’ manufacturing.
launcher stage
complete element of a launcher that delivers the defined thrust during dedicated phase of the launcher mission
- 1 A launcher stage typically consists of a main propulsion system, a reaction controlled system (sometimes integrated to some extend with the main propulsion system), supporting structure, forward and aft skirts, aerodynamic control and/or stabilized surfaces, a separation system and a destruction system.
- 2 Some of the upper stages are also equipped with an avionics system.
- 3 The Ariane 5 upper stage is made of cryogenic main stage (ESC) and vehicle equipment bay (VEB).
launcher system
fully integrated launcher and the needed facilities for manufacturing, testing and delivering the launcher elements
"Fully integrated launcher" means the integrated launcher, including payload, and ready to be launched i.e. all launch control lights on green.
upper part [A5]
made of all the payload adaptor's (ACU), SYLDA or Speltra and Fairing [Ariane 5 launcher]
upper stage [A5]
made of cryogenic main stage (ESC) and vehicle equipment bay (VEB), ending at 1780 diameter interface [Ariane 5 launcher]
Bibliography
|
ECSS-S-ST-00
|
ECSS system – Description, implementation and general requirement.
|
|
EN 45020:2006
|
Standardization and related activities – General vocabulary corrected (ISO/IEC Guide 2:2004)
|
|
ISO 9000:2005
|
Quality management systems - Fundamentals and vocabulary
|
|
ISO 10007:2003
|
Quality management systems - Guidelines for configuration management
|
|
ISO 10795:2011
|
Space systems - Programme management - Vocabulary
|
|
ISO 14623:2003
|
Space systems – Pressure vessels and pressurized structures - Design and operation
|
|
ISO 17666:2003
|
Space systems - Risk management
|
|
ISO 24113:2011
|
Space systems - Space debris mitigation requirements
|
|
ISO/IEC 9126-1:2001
|
Software Engineering – Product Quality – Part 1: Quality Model First Edition
|
|
IEC Multilingual Dictionary – 2001 edition
|
|