
Space product assurance
Nonconformance control system
Foreword
This Standard is one of the series of ECSS Standards intended to be applied together for the management, engineering and product assurance in space projects and applications. ECSS is a cooperative effort of the European Space Agency, national space agencies and European industry associations for the purpose of developing and maintaining common standards. Requirements in this Standard are defined in terms of what shall be accomplished, rather than in terms of how to organize and perform the necessary work. This allows existing organizational structures and methods to be applied where they are effective, and for the structures and methods to evolve as necessary without rewriting the standards.
This Standard has been prepared by the ECSS Executive Secretariat endorsed by the document and discipline focal point and approved by the ECSS Technical Authority
Disclaimer
ECSS does not provide any warranty whatsoever, whether expressed, implied, or statutory, including, but not limited to, any warranty of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose or any warranty that the contents of the item are error-free. In no respect shall ECSS incur any liability for any damages, including, but not limited to, direct, indirect, special, or consequential damages arising out of, resulting from, or in any way connected to the use of this Standard, whether or not based upon warranty, business agreement, tort, or otherwise; whether or not injury was sustained by persons or property or otherwise; and whether or not loss was sustained from, or arose out of, the results of, the item, or any services that may be provided by ECSS.
Published by: ESA Requirements and Standards Division
ESTEC, P.O. Box 299,
2200 AG Noordwijk
The Netherlands
Copyright: 2018 © by the European Space Agency for the members of ECSS
Change log
|
ECSs-Q-20-09A
|
First issue
|
|
ECSS-Q-20-09B
|
Second issue
|
|
ECSS-Q-ST-10-09C
|
Third issue
|
|
ECSS-Q-ST-10-09C Rev.1
|
Third issue, first revision
|
Scope
This Standard defines the requirements for the control of nonconformances.
This Standard applies to all deliverable products and supplies, at all levels, which fail to conform to project requirements.
This Standard is applicable throughout the whole project lifecycle as defined in ECSS-M-ST-10.
This standard may be tailored for the specific characteristics and constrains of a space project in conformance with ECSS-S-ST-00.
Normative references
The following normative documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of this ECSS Standard. For dated references, subsequent amendments to, or revision of any of these publications do not apply, However, parties to agreements based on this ECSS Standard are encouraged to investigate the possibility of applying the more recent editions of the normative documents indicated below. For undated references, the latest edition of the publication referred to applies.
|
ECSS-S-ST-00-01
|
ECSS system – Glossary of terms
|
|
ECSS-Q-ST-20
|
Space product assurance – Quality assurance
|
|
ESCC 22800
|
EEE Nonconformance control system
|
Terms, definitions and abbreviated terms
Terms from other standards
For the purpose of this Standard, the terms and definitions from ECSSST0001 and ECSS-Q-ST-20 apply, in particular for the following terms:
alert
corrective action
critical item
customer
deviation
inspection
nonconformance
preventive action
repair
requirement
rework
supplier
technical expert
verification
waiver
Terms specific to the present standard
major nonconformances
nonconformances which can have an impact on the customer’s requirements in the following areas and cases:
safety of people or equipment,
operational, functional or any technical requirements imposed by the business agreement,
reliability, maintainability, availability,
lifetime,
functional or dimensional interchangeability,
interfaces with hardware or software regulated by different business agreements,
changes to or deviations from approved qualification or acceptance test procedures,
project specific items which are proposed to be scrapped.
minor nonconformances
nonconformances which by definition cannot be classified as major
For example, the following EEE discrepancies after delivery from the manufacturer can be classified as minor:
- random failures, where no risk for a lotrelated reliability or quality problem exists;
- if the form, fit or function are not affected;
- minor inconsistencies in the accompanying documentation.
Abbreviated terms
For the purpose of this Standard, the abbreviated terms from ECSSSST-0001 and the following apply:
|
Abbreviation
|
Meaning
|
|
CIDL
|
configuration item data list
|
|
CIL
|
critical-item list
|
|
COTS
|
commercial offtheshelf
|
|
DJF
|
design justification file
|
|
ECSS
|
European Cooperation for Space Standardization
|
|
EEE
|
electrical, electronic, electromechanical
|
|
FMECA
|
failure mode effect and criticality analysis
|
|
NCR
|
nonconformance report
|
|
NRB
|
nonconformance review board
|
|
PA
|
product assurance
|
|
QA
|
quality assurance
|
|
RAMS
|
reliability, availability, maintainability, safety
|
|
RFD
|
request for deviation
|
|
RFW
|
request for waiver
|
|
SCC
|
space component coordination
|
Nomenclature
The following nomenclature applies throughout this document:
The word “shall” is used in this Standard to express requirements. All the requirements are expressed with the word “shall”.
The word “should” is used in this Standard to express recommendations. All the recommendations are expressed with the word “should”.
It is expected that, during tailoring, recommendations in this document are either converted into requirements or tailored out.
The words “may” and “need not” are used in this Standard to express positive and negative permissions, respectively. All the positive permissions are expressed with the word “may”. All the negative permissions are expressed with the words “need not”.
The word “can” is used in this Standard to express capabilities or possibilities, and therefore, if not accompanied by one of the previous words, it implies descriptive text.
In ECSS “may” and “can” have completely different meanings: “may” is normative (permission), and “can” is descriptive.
The present and past tenses are used in this Standard to express statements of fact, and therefore they imply descriptive text.
Nonconformance control system principles
Process and objectives
The Figure 41 describes the approach to the identification and processing of nonconforming items, which can be performed at each customer/supplier level
This includes:
corrective actions against root causes, to avoid recurrence for other products;
prompt and effective communication between suppliers and customers;
the prevention of nonconformance occurrence, from the analysis of nonconformance records and derived lessons learned.
Detection and immediate actions
When a nonconformance is detected, the project PA representative analyses it to identify its extent and cause. In addition he takes immediate actions to prevent unauthorized use of the nonconforming item. The nonconformance is documented on the NCR form and submitted to the internal NRB.
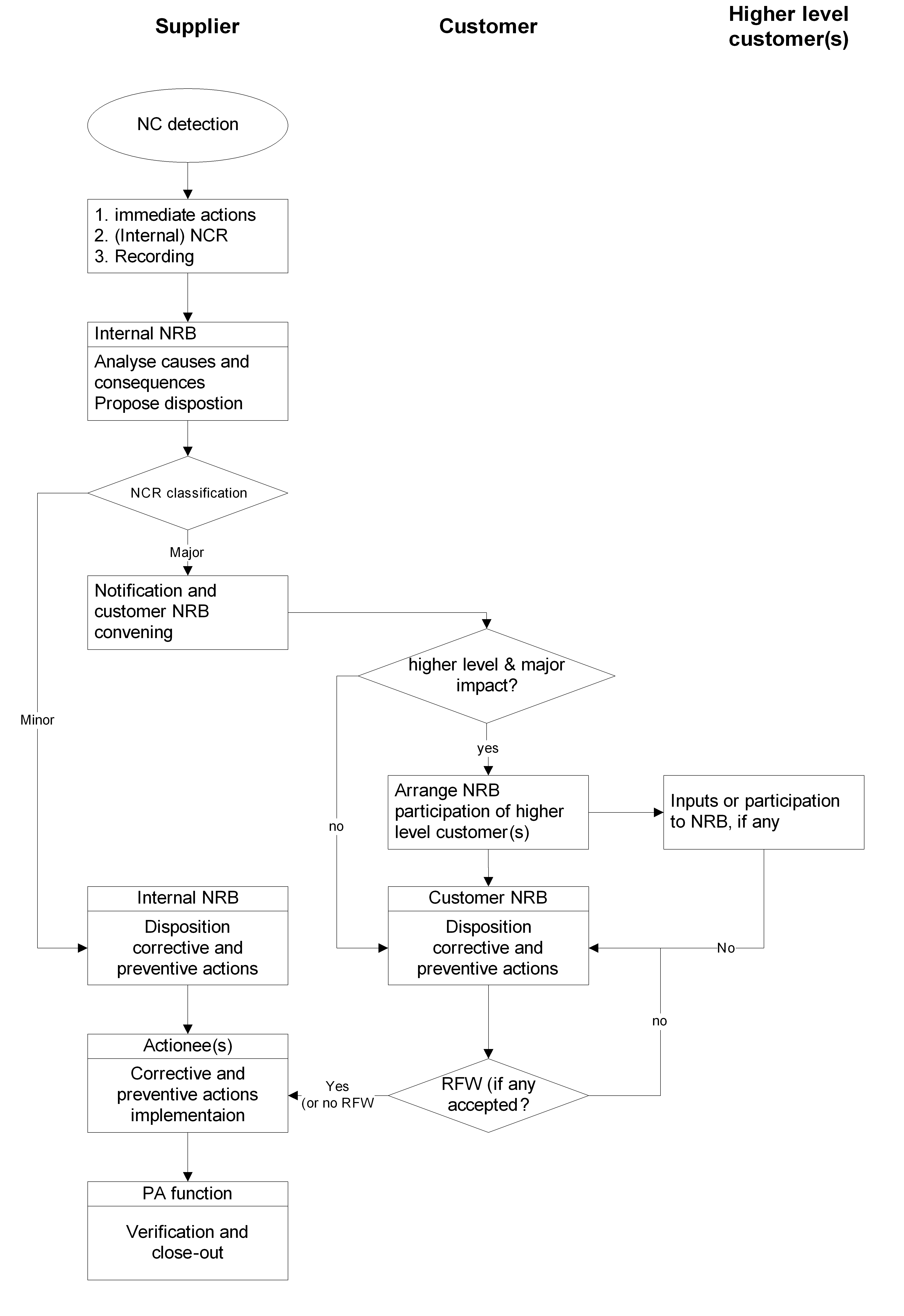 Figure 41: Nonconformance processing flow chart
Figure 41: Nonconformance processing flow chart
Nonconformance review board (NRB)
Internal NRB
The internal NRB investigates the causes and consequences of the nonconformance and classifies the nonconformance either as minor or major.
Furthermore, minor nonconformances are then disposed as follows:
Return to supplier: This disposition only applies to nonconforming procured items.
Use “asis”: The item is found to be usable without eliminating the nonconformance.
Rework: The item is recoverable to conform completely to all specified requirements. Additional work is performed to prepare the item for the rework (e.g. removal of faulty work and cleaning). In no case should the result of earlier applied processes or the precondition for other processes to be applied later on, be affected.
Scrap: The item is not recoverable by rework or repair, for technical or economic reasons.
Repair: The item is recoverable such that it fulfils the intended usage requirements although it does not conform to the originally specified requirements.
The repair procedure is one of the following:
Qualified or standard repair procedure: Those repair procedures which have been approved by the customer in advance for defined applications.
Specific repair procedure: Those repair procedures which are prepared for the specific nonconformance and are approved by the NRB.
Any repair procedure includes the verifications needed to check the repair result.
Major nonconformances are submitted to the customer NRB.
Customer NRB
In principle the customer NRB follows the same process as the internal NRB. In addition, an assessment whether requirements of higher level customers are impacted is performed. If so, these higher level customers are involved in ensuing NRBs. The need for a waiver is also identified and recommended by this NRB.
Multiple internal or customer NRBs can be held before the NCR is closed out.
Corrective and preventive actions
During internal as well as customer NRB, corrective actions are determined to eliminate the causes of the nonconformances. Preventive actions are identified to avoid the occurrence of the nonconformance on similar items.
Implementation of actions and nonconformance close-out
The supplier implements the corrective and/or preventive actions as defined by the NRB.
As soon as all actions are performed and verified, the supplier PA representative closes-out the nonconformance and informs the customer.
Documentation
The supplier documents his implementation of the nonconformance control system.
The supplier’s internal reporting and processing of nonconformances is open and visible to customer reviews and do not delay the processing of the nonconformance in accordance with this Standard.
The supplier may maintain a database of minor and major nonconformances to
followup the NCR,
generate a nonconformance status list (see Annex B),
electronically process the nonconformance.
The amount of information stored should be sufficient to allow statistical and trend analysis.
Nonconformance processing requirements
Detection and immediate actions
The supplier’s project PA representative shall perform an immediate preliminary assessment of the nonconformance to establish its extent and cause when it is detected.
Based on the preliminary assessment the supplier’s project PA representative shall take the following actions without delay:
- Provisions for the safety of the personnel and of the equipment.
- Prevention of unauthorized use of the nonconforming items, by marking and, unless otherwise determined by the PA representative, segregation until their disposition.
- Prevention of the recurrence of the nonconformances on similar or identical items under processing or testing at that time.
This can lead to the suspension of manufacturing or testing.
The supplier shall apply the following actions to the segregation of nonconforming articles:
- Establish a clearly marked holding area for nonconforming items pending NRB disposition.
- Limit the access to this area to NRB members or personnel authorized by the NRB.
- Make provisions to prevent unauthorized removal of any item. For items whose segregation in the holding area is not practicable the supplier shall perform the following actions:
- Mark the item as “not to be used”.
- Make sure that the item can not be used by unauthorized personnel.
The supplier shall complete the nonconformance report in conformance with Annex A, and submit it to the internal NRB.
The supplier shall describe the nonconformance clear, unambiguous and sufficiently detailed that it can be understood by personnel not involved in its detection.
The supplier shall ensure traceability between the NCR and the quality and manufacturing records related to the nonconforming item.
Nonconformance Review Board
General
The NRB shall be the sole technical authority for the treatment of nonconformances occurring in the frame of a business agreement.
All NRB members shall make dispositions and decisions by consensus.
The NRB chairman shall involve higher management levels in case of conflict.
Processing by internal NRB
NRB meeting
The supplier shall nominate and authorize the internal NRBs core members for the business agreement.
The responsibilities and authorities of each member shall be assigned.
The internal NRB shall include, at least, core members from the following areas:
- Project PA (chairman),
- Engineering.
Additional members, or experts, depending on the NCR subject can be nominated by the chairman.
Immediately after the reporting of a nonconformance, the chairman shall convene an internal NRB.
Classification
The internal NRB shall classify nonconformances as major or minor, based on the severity of their consequences.
Classification of nonconformances is not based on their consequences on cost and schedule.
In case of several different minor nonconformances on the same item, the internal NRB shall evaluate whether the nonconformances remain minor or reclassified as “major”.
In case of doubt, the internal NRB shall classify nonconformances as major.
Analysis of causes and consequences
The internal NRB shall investigate the cause(s) of the nonconformance.
If necessary, a separate group of experts can be assigned for the investigation.
The supplier shall carry out physical operation of an irreversible nature on the nonconforming item only with prior approval by the customer.
Nondestructive testing can be used, if the techniques involved have previously been approved by the customer.
The internal NRB shall analyse whether human error or poor workmanship are the primary or secondary cause for the nonconformance.
In case that human error or poor workmanship are the primary or secondary cause for the nonconformance, the supplier shall review all related documents and the competence level of personnel in order to prevent recurrence.
The internal NRB shall investigate the consequences of the nonconformance.
This can be supported, where appropriate, by dependability experts or by documentation such as FMECA, CIL, or DJF.
The internal NRB shall document the results of the investigation in the nonconformance report.
Disposition of minor nonconformances
The internal NRB shall dispose minor nonconformances according to the following criteria:
- Return to supplier
- Use “as-is”
- Rework
- Repair
- Scrap The supplier shall include minor nonconformances in the nonconformance status list.
Unless otherwise stated in the business agreement, the customer is not notified about minor nonconformances.
The supplier shall provide the nonconformance status list to the customer, upon request, for the review of the correct application of classification criteria and appropriate processing.
Processing of major nonconformances
The supplier shall notify the customer each time a nonconformance is classified as “major” within five working days of their detection.
The internal NRB shall submit major nonconformances reports to the customer NRB.
The supplier shall provide a nonconformance report in conformance to Annex A, including a proposed disposition.
Processing by customer NRB
NRB meeting
For major nonconformances the supplier shall include, at least:
- customer’s PA representative (chairman), and
- customer’s engineering representative. The chairman shall nominate additional members, or experts, depending on the NCR subject.
The customer’s representatives can invite observers or consultants from higher customer level, depending on the impacts of the nonconformance.
Assessment of higher level impacts
The customer shall assess whether the requirements of the higher level customer are impacted.
In case of actual or suspected impacts, the customer shall notify his customer and involve him in the ensuing NRB.
Confirmation of causes and consequences
Based on the results of the internal NRB’s investigations, the customer NRB shall decide on the need to perform complementary investigations of causes and consequences.
The customer NRB shall decide if additional analyses are needed from the supplier to assess the cause and consequences of a nonconformance and to support its disposition.
On request of the customer’s NRB, the supplier shall submit the additional analyses to the customer NRB for approval.
The customer NRB shall addresses the following points during the meeting:
- the detailed circumstances of the nonconformance;
- the different analyses, tests or simulations performed to understand the cause of the nonconformance;
- the consequences of the nonconformance. The customer NRB shall determine the consequences of the nonconformance.
Disposition of major nonconformances
The customer NRB shall dispose major nonconformances according to the following criteria:
- Return to supplier
- Use “as-is”
- Rework
- Repair
- Scrap When determining a disposition, the NRB shall perform the following tasks:
- Analyse NCRs and provided analyses
- Review records of any previous similar or identical nonconformances.
- Assess the feasibility of the intended dispositions.
- Assess the applicability of dispositions and corrective actions to existing and in-process items
- Assess the effect of the nonconformance on the requirements of the business agreement
- Assess the effect of the nonconformance on the intended use of the item
- Assess whether the item is identified as critical
- Assess the need for raising an alert to other users of similar nonconforming items, and activate the related procedures established in the business agreement.
NOTE to item 4: This also includes reinspection and retest.
Request for waiver or deviation
The responsible NRB shall identify and recommend the need for a waiver or deviation.
Upon request of the NRB, the supplier shall submit a “request for waiver” for major nonconformances with the “use asis” or “repair” disposition for customer approval.
Upon request of the NRB, the supplier shall submit a “request for deviation” or a “contract change notice, for followon production of the unit.
Corrective and preventive actions
The NRBs shall determine corrective actions to eliminate the cause(s) of the nonconformance and prevent any recurrence.
Typical corrective actions consist of, for instance, changes to tools, equipment, facilities, processes, materials, drawings, specifications, and procedures.
The NRB shall determine also preventive actions to avoid the occurrence of the nonconformance on similar items.
A NCR dispositioned “use asis”, without any physical action performed on the nonconforming item to make it usable, shall be analysed by the NRB to decide the need for preventive actions.
Implementation of actions and nonconformance closeout
Implementation of actions
The supplier shall implement disposition by performing actions defined by the NRB and approved RFWs and RFDs.
The supplier shall re-submit reworked and repaired items to all planned inspections and tests.
Repair can invoke additional inspection and tests, as defined in the applicable repair procedure.
The supplier shall identify and segregate items with “scrap” disposition from all other material within a bonded area under QA supervision.
The supplier shall maintain a list of scrapped items.
The supplier shall establish the traceability to and from the associated NCR of the performance and results of all actions related to a nonconformance.
Nonconformance closeout
The supplier shall closeout an NCR only after the following action have been performed:
- All related actions have been performed and their results successfully verified.
- All defined inspections and tests have been performed, and their results verified and reported on or traceable from the NCR.
- Related RFWs are approved.
The supplier PA representative shall close-out the NCR
For major NCRs, the supplier PA representative shall close-out the NCR only after customer PA endorsement.
After closeout, the supplier shall send a copy of the NCR to the customers involved in its processing.
Documentation
Formats for nonconformance reporting
The customer and the supplier shall agree upon a NCR format to process major nonconformances and nonconformances for customerfurnished equipment.
- 1 The supplier can use his own NCR formats for internal processing as long as they include all data elements designated as mandatory in Annex A.
- 2 The supplier’s working language is acceptable for internal NCRs, unless otherwise required by the business agreement.
The supplier shall maintain a list covering minor and major NCRs, providing a complete representation of the status of all nonconformances occurring in the frame of a business agreement, for each product, at any time.
For each nonconformances, the supplier shall provide a report in conformance with Annex A.
The supplier shall provide the NCR status list as part of the periodic PA status report to the customer, in conformance with Annex B.
The nonconformance status list is usually generated from the nonconformance database.
Nonconformance database
The supplier should maintain a database of nonconformances.
The nonconformance database should be used for the following:
- For NCR followup.
- For the generation of a NCR status list.
- As an electronic tool for complete NCR processing.
NOTE to item 2: Details on the nonconformance status list are provided in Annex B.
The database should contain information related to both minor and major NCRs.
The amount of information stored should be sufficient to allow statistical and trend analysis.
Analysis of records
The supplier shall periodically review the nonconformance records, in order to evaluate the progress of the actions for the correction and prevention of nonconformances and to ensure their closeout.
The nonconformance records shall be analysed to assess the existence of trends in the occurrence of nonconformances.
- 1 This analysis aims at detecting conditions which can lead to new nonconformances and verify the effectiveness of the implementation of the corrective actions performed for previous nonconformances.
- 2 The analysis of records aims at extracting lessons learned, useful for preventing the repetition of mistakes or reinforcing successful practices.
The supplier shall define a frequency of the reviews which is appropriate to the volume of nonconformances, but not less than quarterly.
As result of the analysis of the nonconformance records, the supplier shall provide as a minimum: - total number per flight configuration, subsystem and equipment as appropriate,
- trend of open and closed status, both in terms of disposition and corrective action(s) implementation, and
- number by cause of the nonconformance, to identify the areas for improvement and verify the effectiveness of corrective actions.
The supplier should show the trends separately for hardware, EEE parts and software.
For EEE parts, the supplier should provide the trend per generic type.
Generic types like capacitors, power transistors, microprocessors, carbon resistors, and diodes.
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted, requirement covered by ECSS-Q-ST-60>>
<<deleted, requirement covered by ECSS-Q-ST-60>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted, requirement covered by ECSS-Q-ST-60>>
<<deleted, requirement moved to ECSS-Q-ST-60>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted, requirement moved to ECSS-Q-ST-60>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted, requirement covered by ECSS-Q-ST-80>>
<<deleted, requirement covered by ECSS-Q-ST-80>>
<<deleted, requirement covered by ECSS-Q-ST-80>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted, requirement moved to ECSS-Q-ST-80>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
<<deleted>>
ANNEX(normative)Nonconformance Report – DRD
DRD identification
Requirement identification and source document
This DRD is called by the ECSS-Q-ST-10-09 requirements 5.1e, 5.2.2.5c and 5.5.1c.
Purpose and objective
The purpose of the nonconformance report (NCR) is to provide all relevant information about nonconformances to the NRBs.
Expected response
Scope and content
Company
The NCR shall identify the supplier of the nonconforming item.
Project name
The NCR shall contain the name of the project under which the item is procured.
NCR-no.
The NCR shall provide the unique identification and registration number of the NCR.
Revision
The NCR shall contain alpha or numerical identification of updated issues.
Critical item
The NCR shall identify the criticality of the item by “Yes” or “No” as identified in the project CIL.
Page
The NCR shall contain the individual page number and total number of pages of the report.
Attachments
The NCR shall contain the number of attachments.
Only first page of each item shall be attached to the NCR.
NC item
The NCR shall identify the nonconforming item by name and number according to the CIDL and its serial number (if any).
Drawing no./Part no.
The NCR shall list the document that defines the affected product.
Procedure no.
The NCR shall refer to the procedure in execution when the nonconformance occurs.
Supplier
The NCR shall provide the name of the supplier of the nonconforming item.
Purchase order
The NCR shall provide the number of purchase order if the nonconformance is observed on a supplied product.
NC observation
The NCR shall contain the date and location of the nonconformance observation.
Activity
The NCR shall contain the activity being performed when the nonconformance was detected.
The NCR shall include the name and organization group of the NC observer.
Description
The NCR shall contain a description of the nonconformance, location on the product, means of detection, condition for observation, to be supported by sketches and attachments as appropriate and environmental conditions pertaining to the product at that time.
Initiator
The NCR shall contain the name, date and signature of the person raising the nonconformance.
Internal NRB
The NCR shall list the dispositions and actions agreed by the NRB.
References. to Minutes of Meetings
The NCR shall identify minutes of meeting drafted during the NRB meeting.
Classification
The NCR shall contain the “Minor” or “Major” classification as per internal NRB decision.
Customer notification
The NCR shall contain the date and reference to written notification.
Verification
The NCR shall contain the individual closeout statement by PA personnel for all actions determined by the NRB.
Cause of NC
The NCR shall describe the basic fact or circumstance which causes the nonconformance.
Reference to failure report
The NCR shall provide the document identification number of the failure analysis report.
Corrective or preventive actions
The NCR shall document corrective or preventive actions agreed by internal NRB for minor NCRs.
PA signature
The NCR shall have the date, name and signature of PA representative in the internal NRB.
Engineering signature
The NCR shall have the date, name and signature of the engineering representative in the internal NRB.
Customer NRB dispositions
The NCR shall list the dispositions and actions agreed by the customer NRB.
Finally determined cause of NC
The NCR shall contain the basic fact or circumstances which causes the nonconformance as confirmed by customer NRB.
Reference to Failure Report
The NCR shall contain the document identification number of the failure analysis report on customer NRB level.
Corrective or preventive actions
The NCR shall summarize corrective actions agreed by customer NRB for major NCRs.
Request for waiver
The NCR shall contain “Yes” or “No” based on customer NRB disposition and the identification number of the RFW in case of “Yes”.
Other documents
The NCR shall identify other related documents according to NRB decision.
Chairman
The NCR shall contain the name of company and person chairing the customer NRB.
Members
The NCR shall contain the names of the members of the customer NRB and respective companies.
Chairman signature
The NCR shall have the date and signature of the customer NRB chairman.
Members signature
The NCR shall have the date and signatures of the customer NRB members.
NCR closeout
The NCR shall have the date, signature and stamp of the supplier PA or QA responsible for final closure.
Additional information and continuation sheet
The NCR shall contain any additional information and actions with clear link to the NCR, if additional information is required to describe the nonconformance or its analysis results.
Non mandatory information
The NCR should additionally contain the following information:
- Related internal NCR
- NCR title
- Next higher assembly
- Subsystem / Model reference
- Identification of violated requirements
- Customer notification (date and reference )
- Alert identification
Special remarks
The supplier may use the template given in ECSS-Q-ST-10-09 Annex C.
ANNEX(normative)NCR Status List - DRD
DRD identification
Requirement identification and source document
This DRD is called by the ECSS-Q-ST-10-09 requirement 5.5.1d.
Purpose and objective
The purpose of the NCR status list is to provide a complete representation of the status of all nonconformances occurring in the frame of a business agreement, for each product, at any time.
Expected response
Scope and content
Company
The NCR status shall identify the supplier of the nonconforming item
NCR identifier
The NCR status shall uniquely identify the NCR.
Item identifier
The NCR status shall identify the nonconforming item.
Description
The NCR status shall provide short description of the nonconformance.
Date
The NCR status shall contain the date of last NRB meeting.
Disposition,
The NCR status shall describe the disposition.
Implementation status
The NCR status shall describe the implementation status of the disposition.
RFW
The NCR status shall refer to a RFW, if a related RFW exists.
Status.
The NCR status shall provide the status as “open” or “closed”.
Special remarks
None.
ANNEX(informative)Nonconformance report template
|
Company |
Project Name |
NCR-N: ______________ Revision _____ Related internal NCR-No.: _______________ Critical Item: Yes No Page 1 of ___ Attachments: ____________ |
||||||||||||
|
Nonconformance Report |
||||||||||||||
|
NCR Title |
||||||||||||||
|
NC Item Identification Sr-N |
Drawing No. |
|||||||||||||
|
Next higher Assembly |
Procedure No. |
|||||||||||||
|
Subsystem Model No. |
Supplier Purchase Order |
|||||||||||||
|
NC Observation Date: Location: |
NC detected during .... (Prod.-/Inspec. Step, Test, etc |
|||||||||||||
|
Description of Nonconformance Requirements violated |
||||||||||||||
|
|
Initiator: Date, Name and Signature |
|||||||||||||
|
Internal NRB Dispositions |
Ref. to MoMs |
Classification: Minor Major |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
Customer Notification per |
||||||||||||
|
|
Verification |
|||||||||||||
|
Cause of NC Ref to Failure Report |
Corrective/Preventive Actions |
|
||||||||||||
|
Date:Name:Signature: |
PA |
Engineering |
|
|
||||||||||
|
Customer NRB Dispositions (Class major, only) Ref. to MoMs |
Verification |
|||||||||||||
|
Finally determined Cause of NC Ref to Failure Report |
Corrective/Preventive Actions |
|
||||||||||||
|
Request for Waiver No Yes Reference: ________________ |
Alert No Yes Reference__________________ |
Other related Documents |
||||||||||||
|
NRB Approval Organization/Name |
Chairman |
|
|
|
|
NCR Close out |
||||||||
|
Date, Signature |
|
|
|
|
|
Date, Signature, Stamp |
||||||||
|
Company |
Project Name |
NCR-N: ______________ Revision _____ Page __ of ___ |
|
|
Nonconformance Report - Continuation Sheet - |
|||
|
NCR Treatment Sequence / Findings / Statements / Actions |
Verification |
||
Table: Description of the NCR data requirements
(Part 1 of 3)
|
Box
|
Field
|
Description
|
Mandatory entry
|
|
1
|
Company
|
Identification of the supplier of the nonconforming item
|
Yes
|
|
2
|
Project name
|
Project under which the item is procured
|
Yes
|
|
3
|
NCR-no.
|
Unique identification and registration number
|
Yes
|
|
4
|
Revision
|
Alpha or numerical identification of updated issues
|
Yes
|
|
5
|
Related internal NCR
|
Reference to internal report which might have been issued previously
|
No
|
|
6
|
Critical item
|
“Yes” or “No” as identified in the project CIL
|
Yes
|
|
7
|
Page
|
Individual page number and total number of pages of the report
|
Yes
|
|
|
Attachments
|
Attached pages (only first page of each item)
|
Yes
|
|
8
|
NCR title
|
Short description (it should be the same as used in the nonconformance status list)
|
Yes
|
|
9
|
NC item
|
Identification of the nonconforming item by name and number according to the CIDL and its serial number (if any)
|
Yes
|
|
10
|
Next higher assembly
|
Identification of the assembly group of which the nonconforming product forms part
|
No
|
|
11
|
Subsystem
|
as per 10
|
No
|
|
12
|
Drawing no./Part no.
|
Document that defines the affected product
|
Yes, if applicable
|
|
13
|
Procedure no.
|
Procedure in execution when the nonconformance occurs
|
Yes, if applicable
|
|
14
|
Supplier
|
Name of the supplier of the nonconforming item
|
Yes, if applicable
|
|
15
|
NC observation
|
Date and location of the nonconformance observation
|
Yes
|
|
16
|
NC detected during ...
|
Activity being performed when the nonconformance was detected
|
Yes, where relevant
|
|
17
|
Description
|
Description of the nonconformance, location on the product, means of detection, condition for observation, to be supported by sketches and attachments as appropriate, environmental conditions pertaining to the product at that time
|
Yes
|
|
18
|
Requirements violated
|
Identification of the detailed requirement to which the product does not conform
|
No
|
Table C-1: Description of the NCR data requirements
(Part 2 of 3)
|
19
|
Initiator
|
Name, date and signature of the person raising the nonconformance
|
Yes
|
|
20
|
Internal NRB
|
Dispositions as per clause 5.2.2.4 and actions agreed by the NRB
|
Yes
|
|
21
|
Ref. to MoMs
|
Identification of minutes of meeting drafted during the NRB meeting
|
Yes, if any
|
|
22
|
Classification
|
“Minor” or “Major” as per internal NRB decision
|
Yes
|
|
23
|
Customer notification
|
Date and reference to written notification
|
No
|
|
24
|
Verification
|
Individual closeout statement by PA personnel for all actions determined by the NRB
|
Yes
|
|
25
|
Cause of NC
|
Basic fact or circumstance which causes the nonconformance
|
Yes
|
|
26
|
Ref. to failure report
|
Document identification number of the failure analysis report
|
Yes, if existing
|
|
27
|
Corrective or preventive actions
|
Corrective or preventive actions agreed by internal NRB for minor NCRs
|
Yes
|
|
28
|
PA
|
Date, name and signature of PA representative in the internal NRB
|
Yes
|
|
29
|
Engineering
|
Date, name and signature of the engineering representative in the internal NRB
|
Yes
|
|
30
|
blank
|
Date, names and signatures of additional NRB members of the internal NRB
|
No
|
|
32
|
Customer NRB dispositions
|
Dispositions as per clause 5.2.3.4 and actions agreed by the customer NRB
|
Yes, if class major
|
|
33
|
Finally determined cause of NC
|
Basic fact or circumstances which causes the nonconformance as confirmed by customer NRB
|
Yes, if class major
|
|
34
|
Ref to Failure Report
|
Document identification number of the failure analysis report on customer NRB level
|
Yes, if existing
|
|
35
|
Corrective or preventive actions
|
Corrective actions agreed by customer NRB for major NCRs
|
Yes
|
|
36
|
Request for waiver
|
“Yes” or “No” based on customer NRB disposition and the identification number of the RFW in case of “Yes”
|
Yes, if applicable
|
|
37
|
Alert
|
“Yes” or “No” as per customer NRB decision and the identification number of the Alert in case of “Yes”
|
No
|
|
38
|
Other documents
|
Identification of other related documents according to NRB decision
|
Yes, if applicable
|
|
39
|
Chairman
|
Name of company and person chairing the customer NRB
|
Yes
|
Table C-1: Description of the NCR data requirements
(Part 3 of 3)
|
40to43
|
blank
|
Names of the members of the customer NRB and respective companies
|
Yes
|
|
44
|
blank
|
Date and signature of the customer NRB chairman
|
Yes
|
|
45to48
|
blank
|
Date and signatures of the customer NRB members
|
Yes
|
|
49
|
NCR closeout
|
Date, signature and stamp of the supplier PA or QA responsible for final closure
|
Yes
|
|
50
|
Additional info. /continuation sheet
|
Any additional information and actions with clear link to the NCR
|
Yes, if needed
|
Bibliography
|
ECSS-S-ST-00
|
ECSS system – Description, implementation and general requirements
|
|
ECSS-M-ST-10
|
Space project management – Project planning and implementation
|
|
ECSS-Q-ST-80
|
Space product assurance – Software product assurance
|